Synergistic Targeting of DNA-PK and KIT Signaling Pathways in KIT Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 36682716
- PMCID: PMC9986649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100503
Synergistic Targeting of DNA-PK and KIT Signaling Pathways in KIT Mutant Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
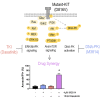
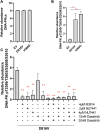
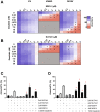
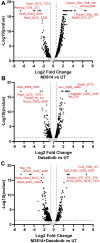
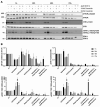
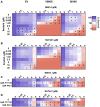
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common and aggressive form of acute leukemia, with a 5-year survival rate of just 24%. Over a third of all AML patients harbor activating mutations in kinases, such as the receptor tyrosine kinases FLT3 (receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3) and KIT (mast/stem cell growth factor receptor kit). FLT3 and KIT mutations are associated with poor clinical outcomes and lower remission rates in response to standard-of-care chemotherapy. We have recently identified that the core kinase of the non-homologous end joining DNA repair pathway, DNA-PK (DNA-dependent protein kinase), is activated downstream of FLT3; and targeting DNA-PK sensitized FLT3-mutant AML cells to standard-of-care therapies. Herein, we investigated DNA-PK as a possible therapeutic vulnerability in KIT mutant AML, using isogenic FDC-P1 mouse myeloid progenitor cell lines transduced with oncogenic mutant KIT (V560G and D816V) or vector control. Targeted quantitative phosphoproteomic profiling identified phosphorylation of DNA-PK in the T2599/T2605/S2608/S2610 cluster in KIT mutant cells, indicative of DNA-PK activation. Accordingly, proliferation assays revealed that KIT mutant FDC-P1 cells were more sensitive to the DNA-PK inhibitors M3814 or NU7441, compared with empty vector controls. DNA-PK inhibition combined with inhibition of KIT signaling using the kinase inhibitors dasatinib or ibrutinib, or the protein phosphatase 2A activators FTY720 or AAL(S), led to synergistic cell death. Global phosphoproteomic analysis of KIT-D816V cells revealed that dasatinib and M3814 single-agent treatments inhibited extracellular signal-regulated kinase and AKT (RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase)/MTOR (serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR) activity, with greater inhibition of both pathways when used in combination. Combined dasatinib and M3814 treatment also synergistically inhibited phosphorylation of the transcriptional regulators MYC and MYB. This study provides insight into the oncogenic pathways regulated by DNA-PK beyond its canonical role in DNA repair and demonstrates that DNA-PK is a promising therapeutic target for KIT mutant cancers.
Keywords: AML; DNA-PK; c-KIT; leukaemia; phosphoproteomics; synergistic targeted therapies.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of protein phosphatase 2A in FLT3+ acute myeloid leukemia cells enhances the cytotoxicity of FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):47465-47478. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10167. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27329844 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted inhibition of cooperative mutation- and therapy-induced AKT activation in AML effectively enhances response to chemotherapy.Leukemia. 2021 Jul;35(7):2030-2042. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-01094-0. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Leukemia. 2021. PMID: 33299144
-
BPR1J373, an Oral Multiple Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Targets c-KIT for the Treatment of c-KIT-Driven Myeloid Leukemia.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Oct;15(10):2323-2333. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-1006. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27512117
-
Oncogenic signaling from the hematopoietic growth factor receptors c-Kit and Flt3.Cell Signal. 2009 Dec;21(12):1717-26. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.06.002. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 19540337 Review.
-
Targeting on glycosylation of mutant FLT3 in acute myeloid leukemia.Hematology. 2019 Dec;24(1):651-660. doi: 10.1080/16078454.2019.1666219. Hematology. 2019. PMID: 31533545 Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond Base Camp: Promise and Pitfalls of PI3K/mTOR Inhibition in Pediatric High- Grade Gliomas.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 May 5:rs.3.rs-6508597. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6508597/v1. Res Sq. 2025. PMID: 40386392 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Emerging role of MYB transcription factors in cancer drug resistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 Apr 30;7:15. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2023.158. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38835346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting N-cadherin (CDH2) and the malignant bone marrow microenvironment in acute leukaemia.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2023 May 3;25:e16. doi: 10.1017/erm.2023.13. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37132370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K/mTOR is a therapeutically targetable genetic dependency in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma.J Clin Invest. 2024 Feb 6;134(6):e170329. doi: 10.1172/JCI170329. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38319732 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteomics profiling of sorafenib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma patient-derived xenografts reveals potential therapeutic strategies.iScience. 2024 Dec 20;28(1):111657. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111657. eCollection 2025 Jan 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39886465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Canberra Cat. No CAN100. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW); Canberra, Australia: 2017. Cancer in Australia 2017.
-
- Lichtman M.A. A historical perspective on the development of the cytarabine (7 days) and daunorubicin (3 days) treatment regimen for acute myelogenous leukemia: 2013 the 40th anniversary of 7+3. Blood Cell Mol. Dis. 2013;50:119–130. - PubMed
-
- Mandelli F., Vignetti M., Suciu S., Stasi R., Petti M.C., Meloni G., et al. Daunorubicin versus mitoxantrone versus idarubicin as induction and consolidation chemotherapy for adults with acute myeloid leukemia: the EORTC and GIMEMA groups study AML-10. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009;27:5397–5403. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Estey E. Acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes in older patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007;25:1908–1915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

