Prognostic implication of a novel right ventricular injury score in septic patients
- PMID: 36683014
- PMCID: PMC10053157
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.14289
Prognostic implication of a novel right ventricular injury score in septic patients
Abstract
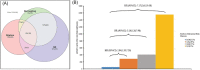
Aims: We aim to investigate the prognostic value of a right ventricular (RV) injury score based on the concept of RV dilation, RV systolic dysfunction, and RV-pulmonary arterial (PA) decoupling in septic patients and to explore whether the RV injury (RVI) score can be used to grade the severity of RV dysfunction in these patients.
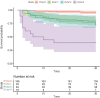
Methods and results: Septic patients admitted to the ICU were prospectively included. We collected haemodynamic and echocardiographic parameters as well as prognostic information. RV dilation was defined as right and left ventricular end-diastolic area ratio (R/LVEDA) > 2/3. RVSD was defined as tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) < 17 mm, right ventricular fractional area change (FAC) < 35%, or peak velocity of tricuspid annulus via tissue Doppler (S') < 10 cm/s. RV-PA decoupling was represented by the TAPSE/pulmonary arterial systolic pressure (PASP) ratio. RVI score were determined by the presence of the following findings: RVSD, RV dilation, and RV-PA decoupling, that is, one point for each finding. A total of 327 patients were enrolled in this study, among whom 276 survived and 51 died at 30 days after admission. Overall, 18.0% had RV dilation, 35.8% had RVSD, and 21.4% had RV-PA decoupling, with an appreciable overlap present. A multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that RV dilation (HR: 2.19, 95% CI: 1.19-4.01, P = 0.011), RVSD (HR: 2.25, 95% CI: 1.23-4.13, P = 0.009) and RV-PA decoupling (HR: 2.08, 95% CI: 1.19-3.65, P = 0.011) were independently associated with a 30 day mortality. Furthermore, RVI score was also an independent predictor, displayed additive effect with respect to 30 day mortality (RVI score 1 vs. RVI score 0, HR: 2.94, 95% CI: 1.20-7.20, P = 0.018; RVI score 2 vs. RVI score 0, HR: 3.20, 95% CI: 1.28-7.98, P = 0.013; RVI score 3 vs. RVI score 0, HR: 7.17, 95% CI: 2.65-19.38, P < 0.001), and had the best performance in model goodness of fit, discrimination and variance explained than the other RV indices.
Conclusions: The RVI score was independently related to 30 day mortality and had the potential to grade the severity of RV dysfunction in septic patients.
Keywords: Echocardiography; Prognosis; Right ventricular dysfunction; Sepsis.
© 2023 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prevalence and prognostic value of various types of right ventricular dysfunction in mechanically ventilated septic patients.Ann Intensive Care. 2021 Jul 13;11(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s13613-021-00902-9. Ann Intensive Care. 2021. PMID: 34255224 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion/Systolic Pulmonary Artery Pressure Ratio for the Assessment of Right Ventricular-Arterial Coupling in Severe Pulmonary Hypertension.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Sep;12(9):e009047. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.119.009047. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31500448 Free PMC article.
-
Right ventricular function and its coupling to pulmonary circulation predicts exercise tolerance in systolic heart failure.ESC Heart Fail. 2022 Feb;9(1):450-464. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13726. Epub 2021 Dec 24. ESC Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 34953062 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of right ventricular free-wall longitudinal strain in patients with pulmonary hypertension: systematic review and meta-analyses.Open Heart. 2024 Feb 7;11(1):e002561. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2023-002561. Open Heart. 2024. PMID: 38325907 Free PMC article.
-
RIGHT VENTRICULAR DYSFUNCTION IN SEPSIS: AN UPDATED NARRATIVE REVIEW.Shock. 2023 Jun 1;59(6):829-837. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002120. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Shock. 2023. PMID: 36943772 Review.
Cited by
-
Can central venous pressure help identify acute right ventricular dysfunction in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients?Ann Intensive Care. 2024 Jul 20;14(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13613-024-01352-9. Ann Intensive Care. 2024. PMID: 39031301 Free PMC article.
-
The value of right ventricular pulmonary artery coupling in determining the prognosis of patients with sepsis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 3;14(1):15283. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65738-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38961249 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of left and right ventricular dysfunction and their clinical outcomes in septic patients.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Jul 29;25(1):364. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-03233-5. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40730941 Free PMC article.
-
IL-2Rα is a potential biomarker for heart failure diagnosis of patients with end-stage renal disease and haemodialysis.ESC Heart Fail. 2025 Feb;12(1):118-132. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.15051. Epub 2024 Sep 12. ESC Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 39263807 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiographic features of right ventricle in septic patients with elevated central venous pressure.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Apr 4;24(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02515-8. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38575875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vieillard‐Baron A, Naeije R, Haddad F, Bogaard HJ, Bull TM, Fletcher N, Lahm T, Magder S, Orde S, Schmidt G, Pinsky MR. Diagnostic workup, etiologies and management of acute right ventricle failure: a state‐of‐the‐art paper. Intensive Care Med. 2018; 44: 774–790. - PubMed
-
- Krishnan S, Schmidt GA. Acute right ventricular dysfunction: real‐time management with echocardiography. Chest. 2015; 147: 835–846. - PubMed
-
- Lahm T, Douglas IS, Archer SL, Bogaard HJ, Chesler NC, Haddad F, Hemnes AR, Kawut SM, Kline JA, Kolb TM, Mathai SC, Mercier O, Michelakis ED, Naeije R, Tuder RM, Ventetuolo CE, Vieillard‐Baron A, Voelkel NF, Vonk‐Noordegraaf A, Hassoun PM. Assessment of right ventricular function in the research setting: knowledge gaps and pathways forward. An official American Thoracic Society research statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018; 198: e15–e43. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sanz J, Sánchez‐Quintana D, Bossone E, Bogaard HJ, Naeije R. Anatomy, function, and dysfunction of the right ventricle: JACC state‐of‐the‐art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019; 73: 1463–1482. - PubMed
-
- Dandel M, Hetzer R. Ventricular systolic dysfunction with and without altered myocardial contractility: clinical value of echocardiography for diagnosis and therapeutic decision‐making. Int J Cardiol. 2021; 327: 236–250. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

