Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4/Midline-1 Axis Promotes T Lymphocyte Motility in Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 36683148
- PMCID: PMC10037965
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202204194
Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4/Midline-1 Axis Promotes T Lymphocyte Motility in Atherosclerosis
Abstract
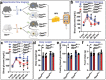
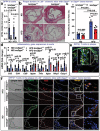
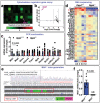
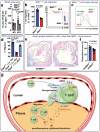
T cells play a crucial role in atherosclerosis, with its infiltration preceding the formation of atheroma. However, how T-cell infiltration is regulated in atherosclerosis remains largely unknown. Here, this work demonstrates that dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) is a novel regulator of T-cell motility in atherosclerosis. Single-cell ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequencing and flow cytometry show that CD4+ T cells in atherosclerotic patients display a marked increase of DPP4. Lack of DPP4 in hematopoietic cells or T cells reduces T-cell infiltration and atherosclerotic plaque volume in atherosclerosis mouse models. Mechanistically, DPP4 deficiency reduces T-cell motility by suppressing the expression of microtubule associated protein midline-1 (Mid1) in T cells. Deletion of either DPP4 or Mid1 inhibits chemokine-induced shape change and motility, while restitution of Mid1 in Dpp4-/- T cell largely restores its migratory ability. Thus, DPP4/Mid1, as a novel regulator of T-cell motility, may be a potential inflammatory target in atherosclerosis.
Keywords: T cell; atherosclerosis; dipeptidyl peptidase-4; midline-1; migration.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- a) White W. B., Cannon C. P., Heller S. R., Nissen S. E., Bergenstal R. M., Bakris G. L., Perez A. T., Fleck P. R., Mehta C. R., Kupfer S., Wilson C., Cushman W. C., Zannad F., Investigators E., N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1327; - PubMed
- b) Scirica B. M., Bhatt D. L., Braunwald E., Steg P. G., Davidson J., Hirshberg B., Ohman P., Frederich R., Wiviott S. D., Hoffman E. B., Cavender M. A., Udell J. A., Desai N. R., Mosenzon O., McGuire D. K., Ray K. K., Leiter L. A., Raz I., Committee S.‐T. S., Investigators , N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1317; - PubMed
- c) Green J. B., Bethel M. A., Armstrong P. W., Buse J. B., Engel S. S., Garg J., Josse R., Kaufman K. D., Koglin J., Korn S., Lachin J. M., McGuire D. K., Pencina M. J., Standl E., Stein P. P., Suryawanshi S., Van de Werf F., Peterson E. D., Holman R. R., Group T. S., N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 232;
- d) Rosenstock J., Kahn S. E., Johansen O. E., Zinman B., Espeland M. A., Woerle H. J., Pfarr E., Keller A., Mattheus M., Baanstra D., Meinicke T., George J. T., von Eynatten M., McGuire D. K., Marx N., Investigators C., JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2019, 322, 1155; - PMC - PubMed
- e) Rosenstock J., Perkovic V., Johansen O. E., Cooper M. E., Kahn S. E., Marx N., Alexander J. H., Pencina M., Toto R. D., Wanner C., Zinman B., Woerle H. J., Baanstra D., Pfarr E., Schnaidt S., Meinicke T., George J. T., von Eynatten M., McGuire D. K., Investigators C., JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2019, 321, 69. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bethel M. A., Patel R. A., Merrill P., Lokhnygina Y., Buse J. B., Mentz R. J., Pagidipati N. J., Chan J. C., Gustavson S. M., Iqbal N., Maggioni A. P., Öhman P., Poulter N. R., Ramachandran A., Zinman B., Hernandez A. F., Holman R. R., Group E. S., Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
