The Case for a Novel Therapeutic Approach to Dementia: Small Molecule Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF/MET) Positive Modulators
- PMID: 36683507
- PMCID: PMC10041442
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-220871
The Case for a Novel Therapeutic Approach to Dementia: Small Molecule Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF/MET) Positive Modulators
Abstract
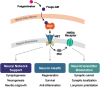
An estimated 6.5 million Americans aged 65 years or older have Alzheimer's disease (AD), which will grow to 13.8 million Americans by 2060. Despite the growing burden of dementia, no fundamental change in drug development for AD has been seen in > 20 years. Currently approved drugs for AD produce only modest symptomatic improvements in cognition with small effect sizes. A growing mismatch exists between the urgent need to develop effective drugs for symptomatic AD and the largely failed search for disease modification. The failure rate of clinical trials in AD is high overall, and in particular for disease-modifying therapies. Research efforts in AD have focused predominantly on amyloid-β and tau pathologies, but limiting clinical research to these "classical hallmarks" of the disease does not address the most urgent patient, caregiver, or societal needs. Rather, clinical research should consider the complex pathophysiology of AD. Innovative approaches are needed that provide outside-the-box thinking, and re-imagine trial design, interventions, and outcomes as well as progress in proteomics and fluid biomarker analytics for both diagnostics and disease monitoring. A new approach offering a highly specific, yet multi-pronged intervention that exerts positive modulation on the HGF/MET neurotrophic system is currently being tested in mid-to-late-stage clinical trials in mild to moderate AD. Findings from such trials may provide data to support novel approaches for development of innovative drugs for treating AD at various disease stages, including among patients already symptomatic, and may offer benefits for other neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; HGF/MET; hepatocyte growth factor; neurodegeneration; neurotrophic; pathogenesis; synaptogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
HJM and KJC are employees of and hold stock in Athira Pharma, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alzheimer's disease; a review of the pathophysiological basis and therapeutic interventions.Life Sci. 2020 Sep 1;256:117996. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117996. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32585249 Review.
-
Fosgonimeton, a Novel Positive Modulator of the HGF/MET System, Promotes Neurotrophic and Procognitive Effects in Models of Dementia.Neurotherapeutics. 2023 Mar;20(2):431-451. doi: 10.1007/s13311-022-01325-5. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Neurotherapeutics. 2023. PMID: 36538176 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of the cerebrospinal fluid hepatocyte growth factor with Alzheimer's disease pathology and cognitive function.BMC Neurol. 2021 Oct 6;21(1):387. doi: 10.1186/s12883-021-02356-9. BMC Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34615471 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329-52. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225010 Review.
-
Agmatine as a novel intervention for Alzheimer's disease: Pathological insights and cognitive benefits.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Apr;96:102269. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102269. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38479477 Review.
Cited by
-
Lewy Body Dementia: An Overview of Promising Therapeutics.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2023 Oct;23(10):581-592. doi: 10.1007/s11910-023-01292-0. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37572228 Review.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association (2022) Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 18, 700–789. - PubMed
-
- van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, Bateman RJ, Chen C, Gee M, Kanekiyo M, Li D, Reyderman L, Cohen S, Froelich L, Katayama S, Sabbagh M, Vellas B, Watson D, Dhadda S, Irizarry M, Kramer LD, Iwatsubo T (2022) Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 388, 9–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

