Opioid and Sedative Coprescription: Prescribing Patterns after an ICU Admission
- PMID: 36683658
- PMCID: PMC9817220
- DOI: 10.4212/cjhp.3245
Opioid and Sedative Coprescription: Prescribing Patterns after an ICU Admission
Abstract
Background: Opioid misuse constitutes a health care crisis in Canada, and coprescription of opioids with sedatives has been associated with adverse events. Opioids and sedatives are frequently administered in the intensive care unit (ICU). The rate of continuation of opioid-sedative combinations after an ICU admission at the study institution was unknown.
Objectives: To determine the rates of opioid and sedative coprescriptions following an ICU admission and to identify factors associated with continuation of hospital-initiated opioid-sedative coprescriptions at ICU transfer and hospital discharge.
Methods: This retrospective chart review involved patients admitted to ICUs at a tertiary care centre between April 1, 2018, and March 31, 2019. Baseline characteristics were obtained from a clinical database and medication information from medication reconciliation forms. An opioid coprescription was defined as prescription of an opioid in combination with a sedative (benzodiazepine, z-drug, gabapentinoid, tricyclic antidepressant, or antipsychotic), and hospital-initiated coprescriptions encompassed various predefined scenarios of therapy started or modified before ICU transfer. Factors associated with hospital-initiated opioid coprescription were analyzed by multivariable logistic regression.
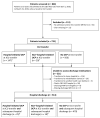
Results: A total of 735 patients met the inclusion criteria. At ICU transfer, 23.0% (169/735) of the patients had an opioid coprescription, and 87.0% (147/169) of these coprescriptions were hospital-initiated. At hospital discharge, 8.6% (44/514) of the patients had an opioid coprescription, and 56.8% (25/44) of these coprescriptions were hospital-initiated. Male sex, home opioid coprescription, surgical patient, prolonged hospital stay, and in-hospital death were significantly associated with hospital-initiated opioid coprescription at the time of ICU transfer. Home opioid coprescription was significantly associated with opioid coprescription at the time of hospital discharge.
Conclusions: Hospital-initiated opioid coprescriptions accounted for the majority of opioid coprescriptions at ICU transfer and hospital discharge. Pharmacists should assess all opioid coprescriptions to determine whether discontinuation and/or dose reduction is appropriate.
Contexte: L’abus d’opioïdes est une crise sanitaire au Canada, et les opioïdes coprescrits avec des sédatifs ont été associés à des événements indésirables. Les opioïdes et les sédatifs sont fréquemment utilisés en unité de soins intensifs (USI). Sur le lieu de l’étude, on ne connaissait pas le taux de maintien de l’utilisation de la combinaison opioïdes-sédatifs après une admission en USI.
Objectifs: Déterminer les taux de coprescription d’opioïdes et de sédatifs suite à une admission en USI et identifier les facteurs associés au maintien de l’utilisation des coprescriptions d’opioïdes et de sédatifs amorcées par l’hôpital au moment du transfert hors de l’USI et du congé hospitalier.
Méthodes: Cet examen rétrospectif des dossiers portait sur des patients admis en USI d’un centre de soins tertiaires entre le 1er avril 2018 et le 31 mars 2019. Les caractéristiques de base ont été obtenues à partir d’une base de données clinique et des informations sur les médicaments à partir des formulaires de bilan comparatif des médicaments. Une coprescription d’opioïdes a été définie comme « La prescription d’un opioïde associée à un sédatif (benzodiazépine, médicament z, gabapentinoïde, antidépresseur tricyclique ou antipsychotique) ». Les « coprescriptions amorcées par l’hôpital » correspondaient à des coprescriptions initiées ou modifiées avant le transfert hors de l’USI, selon des scénarios préalablement définis. Les facteurs associés à la coprescription d’opioïdes amorcée par l’hôpital ont été analysés par régression logistique multivariée.
Résultats: Au total, 735 patients répondaient aux critères d’inclusion. Lors du transfert hors de l’USI, des opioïdes étaient coprescrits à 23,0 % (169/735) d’entre eux; de ces coprescriptions, 87,0 % (147/169) étaient amorcées par l’hôpital. Au moment du congé hospitalier, des opioïdes étaient coprescrits à 8,6 % (44/514) d’entre eux; de ces coprescriptions, 56,8 % (25/44) étaient amorcées par l’hôpital. Le sexe masculin, la coprescription d’opioïdes à domicile, l’admission en chirurgie, le séjour prolongé à l’hôpital et le décès à l’hôpital étaient fortement associés à la coprescription d’opioïdes amorcée par l’hôpital au moment du transfert hors de l’USI. La coprescription d’opioïdes à domicile était fortement associée à la coprescription d’opioïdes au moment du congé de l’hôpital.
Conclusions: Les coprescriptions d’opioïdes amorcées par l’hôpital représentaient la majorité des coprescriptions au moment du transfert hors de l’USI et au moment du congé de l’hôpital. Les pharmaciens doivent évaluer toutes les coprescriptions d’opioïdes pour déterminer si l’arrêt et/ou la réduction de la dose est appropriée.
Keywords: associated factors; critical care; intensive care; opioid; opioid coprescription; sedative.
2023 Canadian Society of Hospital Pharmacists. All content in the Canadian Journal of Hospital Pharmacy is copyrighted by the Canadian Society of Hospital Pharmacy. In submitting their manuscripts, the authors transfer, assign, and otherwise convey all copyright ownership to CSHP.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Area Deprivation Index and Coprescription of Opioids and Sedative Hypnotics.Cureus. 2025 Mar 11;17(3):e80422. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80422. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40213765 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Opioid and Psychotropic Prescription in Pregnancy in the United States From 2001 to 2015 in a Privately Insured Population : A Cross-sectional Study.Ann Intern Med. 2020 Dec 1;173(11 Suppl):S19-S28. doi: 10.7326/M19-3249. Ann Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 33253018
-
Discharge prescribing of enteral opioids in opioid naïve patients following non-surgical intensive care: A retrospective cohort study.J Crit Care. 2022 Apr;68:16-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.10.021. Epub 2021 Nov 29. J Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 34856489 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of dexmedetomidine versus propofol on extubation times, length of stay and mortality rates in adult cardiac surgery patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2018 May;16(5):1220-1239. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003488. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2018. PMID: 29762314
-
Association of opioid exposure during intensive care unit stays with post-discharge opioid use: A retrospective study and literature review.J Opioid Manag. 2021 Nov-Dec;17(6):511-516. doi: 10.5055/jom.2021.0685. J Opioid Manag. 2021. PMID: 34904699 Review.
References
-
- Pan-Canadian trends in the prescribing of opioids and benzodiazepines, 2012 to 2017. Canadian Institute for Health Information; 2018. [cited 2020 Nov 8]. Available from: https://www.cihi.ca/sites/default/files/document/opioid-prescribing-june....
-
- Devlin JW, Skrobik Y, Gélinas C, Needham DM, Slooter AJC, Pandharipande PP, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and management of pain, agitation/sedation, delirium, immobility, and sleep disruption in adult patients in the ICU. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(9):e825–73. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003299. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
