Recent advances in immunoassay technologies for the detection of human coronavirus infections
- PMID: 36683684
- PMCID: PMC9845787
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1040248
Recent advances in immunoassay technologies for the detection of human coronavirus infections
Abstract
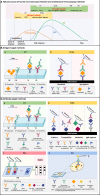
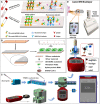
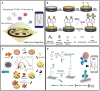
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the seventh coronavirus (CoV) that has spread in humans and has become a global pandemic since late 2019. Efficient and accurate laboratory diagnostic methods are one of the crucial means to control the development of the current pandemic and to prevent potential future outbreaks. Although real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) is the preferred laboratory method recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for diagnosing and screening SARS-CoV-2 infection, the versatile immunoassays still play an important role for pandemic control. They can be used not only as supplemental tools to identify cases missed by rRT-PCR, but also for first-line screening tests in areas with limited medical resources. Moreover, they are also indispensable tools for retrospective epidemiological surveys and the evaluation of the effectiveness of vaccination. In this review, we summarize the mainstream immunoassay methods for human coronaviruses (HCoVs) and address their benefits, limitations, and applications. Then, technical strategies based on bioinformatics and advanced biosensors were proposed to improve the performance of these methods. Finally, future suggestions and possibilities that can lead to higher sensitivity and specificity are provided for further research.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; diagnosis; human coronavirus; immunosensor; serological testing methods.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Chen, Xiang, Hu, Zhan, Yu, Zhang, Wu, Liu, Kai and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Monitoring Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Review of Available Diagnostic Tools.Front Public Health. 2021 Jun 7;9:672215. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.672215. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34164371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Universal screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013718. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013718. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33502003 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and evaluation of a quadruple quantitative real-time PCR assay for simultaneous detection of human coronavirus subtypes.Virol J. 2022 Apr 11;19(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01793-3. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 35410305 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic strategy combining high throughput quantitative antigen immunoassay and real time PCR.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2023 Mar 22;61(9):1661-1669. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2023-0087. Print 2023 Aug 28. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2023. PMID: 36947812
-
In vitro diagnostics of coronavirus disease 2019: Technologies and application.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021 Apr;54(2):164-174. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.05.016. Epub 2020 Jun 5. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2021. PMID: 32513617 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tapered Fiber Bioprobe Based on U-Shaped Fiber Transmission for Immunoassay.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Oct 20;13(10):940. doi: 10.3390/bios13100940. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887133 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological assessment of NSFu1: A novel fusion molecule constructed from structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2 for improving COVID-19 antibody detection.Arch Microbiol. 2025 Mar 15;207(4):88. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04286-3. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40088274
-
On-site detection of infectious disease based on CaCO3-based magnetic micromotor integrated with graphene field effect transistor.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Apr 11;191(5):257. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06345-w. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38600405
References
-
- Abela I. A., Pasin C., Schwarzmuller M., Epp S., Sickmann M. E., Schanz M. M., et al. . (2021). Multifactorial seroprofiling dissects the contribution of pre-existing human coronaviruses responses to SARS-CoV-2 immunity. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 6703. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27040-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad T. A., Eweida A. E., Sheweita S. A. (2016). B-cell epitope mapping for the design of vaccines and effective diagnostics. Trials Vaccinol. 5, 71–83. doi: 10.1016/j.trivac.2016.04.003 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

