Unveiling the biological role of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulators in inflammatory bowel diseases
- PMID: 36683721
- PMCID: PMC9850947
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.110
Unveiling the biological role of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulators in inflammatory bowel diseases
Abstract
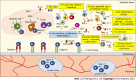
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract that has a high epidemiological prevalence worldwide. The increasing disease burden worldwide, lack of response to current biologic therapeutics, and treatment-related immunogenicity have led to major concerns regarding the clinical management of IBD patients and treatment efficacy. Understanding disease pathogenesis and disease-related molecular mechanisms is the most important goal in developing new and effective therapeutics. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor (S1PR) modulators form a class of oral small molecule drugs currently in clinical development for IBD have shown promising effects on disease improvement. S1P is a sphingosine-derived phospholipid that acts by binding to its receptor S1PR and is involved in the regulation of several biological processes including cell survival, differentiation, migration, proliferation, immune response, and lymphocyte trafficking. T lymphocytes play an important role in regulating inflammatory responses. In inflamed IBD tissue, an imbalance between T helper (Th) and regulatory T lymphocytes and Th cytokine levels was found. The S1P/S1PR signaling axis and metabolism have been linked to inflammatory responses in IBD. S1P modulators targeting S1PRs and S1P metabolism have been developed and shown to regulate inflammatory responses by affecting lymphocyte trafficking, lymphocyte number, lymphocyte activity, cytokine production, and contributing to gut barrier function.
Keywords: Immune responses; Inflammatory bowel disease; Intestinal inflammation; Modulators; Sphingosine 1 phosphate; Sphingosine-1-phosphate; T helper 1/T helper 17.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There is no conflict of interest associated with the senior author or any of the other coauthors who contributed their efforts in this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting the Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Pathway: New Opportunities in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Management.Drugs. 2024 Oct;84(10):1179-1197. doi: 10.1007/s40265-024-02094-5. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39322927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review article: the sphingosine 1 phosphate/sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor axis - a unique therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel disease.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Feb;55(3):277-291. doi: 10.1111/apt.16741. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34932238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) signaling regulates the production of intestinal IgA and its potential role in the pathogenesis of canine inflammatory bowel disease.J Vet Med Sci. 2019 Sep 3;81(9):1249-1258. doi: 10.1292/jvms.19-0016. Epub 2019 Jul 25. J Vet Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31341112 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling in Immune-Mediated Diseases: Beyond Multiple Sclerosis.Drugs. 2021 Jun;81(9):985-1002. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01528-8. Epub 2021 May 13. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33983615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Trends Mol Med. 2017 Apr;23(4):362-374. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.02.002. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Trends Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28283249 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunity in digestive diseases: new drugs for inflammatory bowel disease treatment-insights from Phase II and III trials.J Gastroenterol. 2024 Sep;59(9):761-787. doi: 10.1007/s00535-024-02130-x. Epub 2024 Jul 9. J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38980426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Etrasimod in Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis: A Comprehensive Review.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 2;36(6):336-342. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2025.25148. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40501185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroacupuncture Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-reperfusion Injury by Regulating the S1PR2/TLR4/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway via m6A Methylation of lncRNA H19.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2024;21(1):64-73. doi: 10.2174/0115672026294183240207115956. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 38409728
-
Navigating new horizons in inflammatory bowel disease: Integrative approaches and innovations.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov 7;30(41):4411-4416. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i41.4411. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39534414 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure of Helicobacter pylori to clarithromycin in vitro resulting in the development of resistance and triggers metabolic reprogramming associated with virulence and pathogenicity.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 6;19(3):e0298434. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298434. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38446753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coward S, Clement F, Benchimol EI, Bernstein CN, Avina-Zubieta JA, Bitton A, Carroll MW, Hazlewood G, Jacobson K, Jelinski S, Deardon R, Jones JL, Kuenzig ME, Leddin D, McBrien KA, Murthy SK, Nguyen GC, Otley AR, Panaccione R, Rezaie A, Rosenfeld G, Peña-Sánchez JN, Singh H, Targownik LE, Kaplan GG. Past and Future Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Based on Modeling of Population-Based Data. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1345–1353.e4. - PubMed
-
- Singh S, George J, Boland BS, Vande Casteele N, Sandborn WJ. Primary Non-Response to Tumor Necrosis Factor Antagonists is Associated with Inferior Response to Second-line Biologics in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Crohns Colitis. 2018;12:635–643. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Olivera P, Danese S, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Next generation of small molecules in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 2017;66:199–209. - PubMed
-
- Argollo M, Fiorino G, Hindryckx P, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Danese S. Novel therapeutic targets for inflammatory bowel disease. J Autoimmun. 2017;85:103–116. - PubMed
-
- Sukocheva OA, Lukina E, McGowan E, Bishayee A. Sphingolipids as mediators of inflammation and novel therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel disease. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020;120:123–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

