Integrated printed BDNF-stimulated HUCMSCs-derived exosomes/collagen/chitosan biological scaffolds with 3D printing technology promoted the remodelling of neural networks after traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 36683754
- PMCID: PMC9847532
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbac085
Integrated printed BDNF-stimulated HUCMSCs-derived exosomes/collagen/chitosan biological scaffolds with 3D printing technology promoted the remodelling of neural networks after traumatic brain injury
Abstract
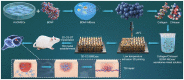
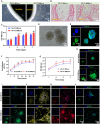
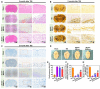
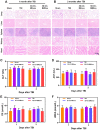
The restoration of nerve dysfunction after traumatic brain injury (TBI) faces huge challenges due to the limited self-regenerative abilities of nerve tissues. In situ inductive recovery can be achieved utilizing biological scaffolds combined with endogenous human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HUCMSCs)-derived exosomes (MExos). In this study, brain-derived neurotrophic factor-stimulated HUCMSCs-derived exosomes (BMExos) were composited with collagen/chitosan by 3D printing technology. 3D-printed collagen/chitosan/BMExos (3D-CC-BMExos) scaffolds have excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Subsequently, in vivo experiments showed that 3D-CC-BMExos therapy could improve the recovery of neuromotor function and cognitive function in a TBI model in rats. Consistent with the behavioural recovery, the results of histomorphological tests showed that 3D-CC-BMExos therapy could facilitate the remodelling of neural networks, such as improving the regeneration of nerve fibres, synaptic connections and myelin sheaths, in lesions after TBI.
Keywords: BDNF; chitosan; collagen; exosomes; mesenchymal stem cell; traumatic brain injury.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures





References
-
- Qian F, Han Y, Han Z, Zhang D, Zhang L, Zhao G, Li S, Jin G, Yu R, Liu H.. In situ implantable, post-trauma microenvironment-responsive, ROS depletion hydrogels for the treatment of traumatic brain injury. Biomaterials 2021;270:120675. - PubMed
-
- Ma S, Zhou J, Huang T, Zhang Z, Xing Q, Zhou X, Zhang K, Yao M, Cheng T, Wang X, Wen X, Guan F.. Sodium alginate/collagen/stromal cell-derived factor-1 neural scaffold loaded with BMSCs promotes neurological function recovery after traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater 2021;131:185–97. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Zhang D, Guo S, Zhao C, Wang L, Ma S, Guan F, Yao M.. Dual-enzymatically cross-linked gelatin hydrogel promotes neural differentiation and neurotrophin secretion of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of moderate traumatic brain injury. Int J Biol Macromol 2021;187:200–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

