Functional engineering strategies of 3D printed implants for hard tissue replacement
- PMID: 36683758
- PMCID: PMC9845531
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbac094
Functional engineering strategies of 3D printed implants for hard tissue replacement
Abstract
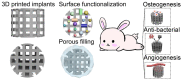
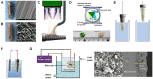
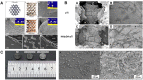
Three-dimensional printing technology with the rapid development of printing materials are widely recognized as a promising way to fabricate bioartificial bone tissues. In consideration of the disadvantages of bone substitutes, including poor mechanical properties, lack of vascularization and insufficient osteointegration, functional modification strategies can provide multiple functions and desired characteristics of printing materials, enhance their physicochemical and biological properties in bone tissue engineering. Thus, this review focuses on the advances of functional engineering strategies for 3D printed biomaterials in hard tissue replacement. It is structured as introducing 3D printing technologies, properties of printing materials (metals, ceramics and polymers) and typical functional engineering strategies utilized in the application of bone, cartilage and joint regeneration.
Keywords: 3D printing; additive manufacturing; bone regeneration; functional engineering; hard tissue replacement.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures




References
-
- Roseti L, Parisi V, Petretta M, Cavallo C, Desando G, Bartolotti I, Grigolo B.. Scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: state of the art and new perspectives. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 2017;78:1246–62. - PubMed
-
- Marie P. Physiology of bone tissue. Immuno-Anal Biol Spec 1992;7:17–24.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

