Developability assessment at early-stage discovery to enable development of antibody-derived therapeutics
- PMID: 36683767
- PMCID: PMC9847343
- DOI: 10.1093/abt/tbac029
Developability assessment at early-stage discovery to enable development of antibody-derived therapeutics
Abstract
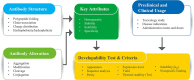
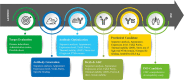
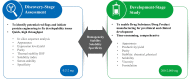
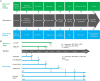
Developability refers to the likelihood that an antibody candidate will become a manufacturable, safe and efficacious drug. Although the safety and efficacy of a drug candidate will be well considered by sponsors and regulatory agencies, developability in the narrow sense can be defined as the likelihood that an antibody candidate will go smoothly through the chemistry, manufacturing and control (CMC) process at a reasonable cost and within a reasonable timeline. Developability in this sense is the focus of this review. To lower the risk that an antibody candidate with poor developability will move to the CMC stage, the candidate's developability-related properties should be screened, assessed and optimized as early as possible. Assessment of developability at the early discovery stage should be performed in a rapid and high-throughput manner while consuming small amounts of testing materials. In addition to monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, multispecific antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates, as the derivatives of monoclonal antibodies, should also be assessed for developability. Moreover, we propose that the criterion of developability is relative: expected clinical indication, and the dosage and administration route of the antibody could affect this criterion. We also recommend a general screening process during the early discovery stage of antibody-derived therapeutics. With the advance of artificial intelligence-aided prediction of protein structures and features, computational tools can be used to predict, screen and optimize the developability of antibody candidates and greatly reduce the risk of moving a suboptimal candidate to the development stage.
Keywords: antibody; antibody-drug conjugate; bispecific; developability; discovery.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Antibody Therapeutics. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Weijie Zhang, Hao Wang, Nan Feng, Yifeng Li, Jijie Gu and Zhuozhi Wang are current employees of WuXi Biologics and may hold WuXi Biologics’ stocks.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessment of Therapeutic Antibody Developability by Combinations of In Vitro and In Silico Methods.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2313:57-113. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1450-1_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34478132
-
Predicting Antibody Developability Profiles Through Early Stage Discovery Screening.MAbs. 2020 Jan-Dec;12(1):1743053. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2020.1743053. MAbs. 2020. PMID: 32249670 Free PMC article.
-
Biologics developability data analysis using hierarchical clustering accelerates candidate lead selection, optimization, and preformulation screening.MAbs. 2025 Dec;17(1):2502127. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2025.2502127. Epub 2025 May 10. MAbs. 2025. PMID: 40347482 Free PMC article.
-
Developability assessment during the selection of novel therapeutic antibodies.J Pharm Sci. 2015 Jun;104(6):1885-1898. doi: 10.1002/jps.24430. Epub 2015 Mar 26. J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 25821140 Review.
-
Current advances in biopharmaceutical informatics: guidelines, impact and challenges in the computational developability assessment of antibody therapeutics.MAbs. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2020082. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2021.2020082. MAbs. 2022. PMID: 35104168 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Accelerating antibody discovery and optimization with high-throughput experimentation and machine learning.J Biomed Sci. 2025 May 9;32(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12929-025-01141-x. J Biomed Sci. 2025. PMID: 40346589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing computational technologies to facilitate antibody-drug conjugate development.Nat Chem Biol. 2025 Aug;21(8):1138-1147. doi: 10.1038/s41589-025-01950-z. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Nat Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 40579571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Druggability properties of a L309K mutation in the antibody CH2 domain.3 Biotech. 2024 Jun;14(6):152. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04000-y. Epub 2024 May 11. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 38742229 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of bispecific antibodies with optimal developability using FcRn‑Ph‑HPLC as an optimized FcRn affinity chromatography method.MAbs. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2245519. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2023.2245519. MAbs. 2023. PMID: 37599441 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of monoclonal antibody viscosity using interpretable machine learning.MAbs. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2303781. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2303781. Epub 2024 Mar 12. MAbs. 2024. PMID: 38475982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vlasak, J, Bussat, MC, Wang, S et al. Identification and characterization of asparagine deamidation in the light chain CDR1 of a humanized IgG1 antibody. Anal Biochem 2009; 392: 145–54. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
