Severe pediatric Mycoplasma pneumonia as the cause of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage requiring veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A case report
- PMID: 36683817
- PMCID: PMC9858565
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.925655
Severe pediatric Mycoplasma pneumonia as the cause of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage requiring veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A case report
Abstract
Background: Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH) is an acute life-threatening disease often associated with immunocompromised patients and systemic disorders, such as infections, vasculitis, and toxins. Mycoplasma pneumoniae is one of the most common causes of community-acquired pneumonia in children, which rarely causes respiratory failure and fulminant disease; However, a rapid progression may occur in some patients. Mycoplasma pneumonia-associated DAH is rare.
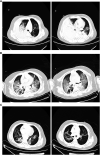
Case presentation: We report a case of severe pediatric mycoplasma pneumonia in an immuno-competent child. This patient's condition progressed rapidly, with severe lung lesions associated with pleural effusion, coagulopathy, diffuse alveolar haemorrhage and severe respiratory distress requiring ventilator and intravenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO) support. She was discharged upon successful treatment.
Conclusion: Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children is very rare, and clinicians should be aware of the potential rapid onset of the disease. Early detection and diagnosis are very important. The main treatment measures include anti-infection and supportive measures such as mechanical ventilation, but as in our case, success with both prone positioning for more than 10 h per day and VV-ECMO was life-saving.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; diffuse alveolar hemorrhage; mNGS; mycoplasma pneumoniae; pediatric; veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
© 2023 Zhang and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO) for life-threatening isolated pulmonary anti-GBM disease.Respir Med Case Rep. 2022 Jun 1;38:101680. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2022.101680. eCollection 2022. Respir Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35677578 Free PMC article.
-
Early diagnosis and appropriate respiratory support for Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia associated acute respiratory distress syndrome in young and adult patients: a case series from two centers.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 May 24;20(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05085-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32448200 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of extracorporeal life support for diffuse alveolar damage and diffuse alveolar hemorrhage: A systematic review.Artif Organs. 2021 Jun;45(6):559-568. doi: 10.1111/aor.13861. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Artif Organs. 2021. PMID: 33190331
-
The role of extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in the treatment of diffuse alveolar haemorrhage secondary to ANCA-associated vasculitis: report of two cases and review of the literature.Rheumatol Int. 2019 Feb;39(2):367-375. doi: 10.1007/s00296-018-4116-z. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Rheumatol Int. 2019. PMID: 30074077 Review.
-
A rare case of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage caused by acute mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2021 May 10;11(3):366-369. doi: 10.1080/20009666.2021.1906491. eCollection 2021. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2021. PMID: 34234908 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Optimization strategy for the early timing of bronchoalveolar lavage treatment for children with severe mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Oct 5;23(1):661. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08619-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37798699 Free PMC article.
-
Successful treatment of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage secondary to Mycoplasma pneumoniae complicated with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in children: a case report and non-systematic literature review.Front Pediatr. 2024 Jul 10;12:1404872. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1404872. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39049845 Free PMC article.
-
Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Due to Macrolide-Refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae Diagnosed by FilmArray Analysis of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid.Cureus. 2024 Dec 11;16(12):e75525. doi: 10.7759/cureus.75525. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39803058 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of an early comprehensive assessment model for refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia and internal validation.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 May 24;25(1):744. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11133-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40413448 Free PMC article.
-
Fulminant fatal pneumonia and bacteremia due to Aeromonas dhakensis in an immunocompetent man: a case report and literature review.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jul 15;14:1359422. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1359422. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39077434 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shah SS. Mycoplasma pneumoniae. In: Long S, Pickering LK, Prober CG, editors. Principle and practice of pediatric infectious diseases. 4th ed.–7e5, London: Churchill Livingstone; (2012). 993 p.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

