14-3-3η protein is associated with disease activity and osteoporosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 36683839
- PMCID: PMC9847109
- DOI: 10.5114/reum.2022.123669
14-3-3η protein is associated with disease activity and osteoporosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: This study was designed to explore the potential association of serum 14-3-3η protein level with disease activity and bone mineral density (BMD) in Egyptian patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Patients were recruited from the outpatient clinic at Mansoura University Hospital.
Material and methods: One hundred eighty-eight patients with RA and 192 matched controls were enrolled. The rheumatoid arthritis activity parameters were evaluated in RA patients. Bone mineral density was measured. Serum levels of 14-3-3η protein and IL-6 were estimated for all participants by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA).
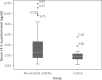
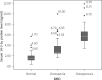
Results: Rheumatoid arthritis patients had a significantly higher median serum 14-3-3η protein level compared to matched controls (p ≤ 0.05). Serum level of 14-3-3η protein was significantly correlated with DAS28-ESR (p ≤ 0.05) and serum IL-6 level (p ≤ 0.05). The rheumatoid arthritis-osteoporosis group had significantly higher serum 14-3-3η protein than the RA-osteopenia group and RA-control group. Similarly, the difference of the serum 14-3-3η protein between the RA-osteopenia group and the RA-control group was significant. In the linear regression analysis, the strongest factors that were associated with BMD in RA patients were the serum level of 14-3-3η protein (p ≤ 0.05), IL-6 (p ≤ 0.05) and DAS28-ESR (p ≤ 0.05).
Conclusions: Serum level of 14-3-3η protein was significantly elevated in RA patients compared to controls and is significantly correlated with parameters of activity disease. The RA-osteoporosis group had significantly higher serum 14-3-3η protein than the RA-osteopenia group and RA-control group. Serum 14-3-3η protein can be a promising biomarker to reflect RA activity and predict presence of osteoporosis in RA patients.
Keywords: 14-3-3η protein; diseases activity score; osteoporosis; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright: © 2022 Narodowy Instytut Geriatrii, Reumatologii i Rehabilitacji w Warszawie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated serum 14-3-3η protein may be helpful for diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis associated with secondary osteoporosis in Chinese population.Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Nov;36(11):2581-2587. doi: 10.1007/s10067-017-3807-2. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28875246
-
The association among 14-3-3η protein, inflammation, bone remodeling and osteoporosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Pak J Med Sci. 2020 Jul-Aug;36(5):872-876. doi: 10.12669/pjms.36.5.2403. Pak J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32704255 Free PMC article.
-
Serum 14-3-3η Could Improve the Diagnostic Rate of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Correlates to Disease Activity.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2019 Jan;49(1):57-62. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2019. PMID: 30814078
-
14-3-3η: a novel biomarker platform for rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014 Sep-Oct;32(5 Suppl 85):S-35-9. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25365087 Review.
-
14-3-3η protein: a promising biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis.Biomark Med. 2018 Aug;12(8):917-925. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2017-0385. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Biomark Med. 2018. PMID: 30022679 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical significance of long non-coding RNA NORAD in rheumatoid arthritis.Adv Rheumatol. 2024 Jan 18;64(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s42358-024-00349-z. Adv Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38238863
-
Serum 14‑3‑3η levels are increased and associated with a higher risk of osteoporosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta‑analysis.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Dec 27;27(2):76. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12364. eCollection 2024 Feb. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 38264428 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous