Standardized ileal digestible lysine requirements based on growth performance and histochemical characteristics of male broilers from 10 to 21 d of age
- PMID: 36683880
- PMCID: PMC9841227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aninu.2022.09.012
Standardized ileal digestible lysine requirements based on growth performance and histochemical characteristics of male broilers from 10 to 21 d of age
Abstract
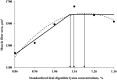
The growth performance and histochemical characteristics of breast muscle fibers were used to estimate the standardized ileal digestible (SID) Lys requirements for 10- to 21-d-old male broilers. Three hundred and sixty 10-d-old Ross 308 broilers (290 ± 16.6 g) were allocated to 6 diets in a randomized complete block design with 6 replicate cages per treatment and 10 birds per cage. The 6 experimental diets were formulated to contain equally spaced increasing levels of SID Lys from 0.86% to 1.36%. The data were analyzed using the MIXED procedure of SAS. The Lys requirements were estimated by the NLIN procedure of SAS. An increase in dietary SID Lys from 0.86% to 1.36% resulted in a quadratic increase (P < 0.05) in body weight gain (BWG), gain to feed ratio (G:F), breast weight, muscle cross-sectional area (MCSA), and fiber area. The SID Lys requirements based on the one-slope broken-line, quadratic line, the first intercept between the plateau of the one-slope broken-line and quadratic-line models and 95% of the upper asymptote of the quadratic-line model were estimated to be 1.01%, 1.19%, 1.08%, and 1.13% for BWG, 1.06%, 1.22%, 1.11%, and 1.16% for G:F, 1.10%, 1.29%, 1.19%, and 1.22% for breast weight, 1.06%, 1.22%, 1.12%, and 1.16% for MCSA, and 1.14%, 1.22%, 1.16%, and 1.16% for breast muscle fiber area, respectively. It was concluded that the SID Lys requirements for broilers at the age of 10 to 21 d depended on the response variables used for estimation, and that histochemical characteristics of breast muscle fibers could be good indicators for estimating SID Lys requirements.
Keywords: Broiler chicken; Growth performance; Lysine; Muscle fiber characteristics; Requirement.
© 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co. Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Standardized ileal digestible methionine requirements for 22 to 29-d-old male broilers based on the growth performance and feather development.J Anim Sci Technol. 2024 May;66(3):555-566. doi: 10.5187/jast.2023.e139. Epub 2024 May 31. J Anim Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 38975574 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the standardized ileal digestible calcium requirement of Ross broilers from hatch to day 14 post-hatch.Anim Nutr. 2023 Dec 20;16:122-129. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.06.016. eCollection 2024 Mar. Anim Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38357570 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of the standardized ileal digestible valine to lysine ratio required for 25- to 120-kilogram pigs fed low crude protein diets supplemented with crystalline amino acids.J Anim Sci. 2015 Oct;93(10):4761-73. doi: 10.2527/jas.2015-9308. J Anim Sci. 2015. PMID: 26523569 Clinical Trial.
-
Estimation of the optimal ratio of standardized ileal digestible threonine to lysine for finishing barrows fed low crude protein diets.Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2013 Aug;26(8):1172-80. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2013.13045. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2013. PMID: 25049898 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of standardized ileal digestible lysine requirement of nursery pigs from seven to fourteen kilograms.J Anim Sci. 2012 Dec;90(12):4380-90. doi: 10.2527/jas.2011-5131. J Anim Sci. 2012. PMID: 23255816 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Effects of duo-strain probiotics on growth, digestion, and gut health in broiler chickens.Vet Anim Sci. 2024 Mar 2;24:100343. doi: 10.1016/j.vas.2024.100343. eCollection 2024 Jun. Vet Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 38525085 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of Optimal and Maximum Standardized Ileal Digestible Methionine Requirements Based on Performance for Male Broilers Aged 0 to 21 Days.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jan 20;15(2):278. doi: 10.3390/ani15020278. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858279 Free PMC article.
-
Standardized ileal digestible lysine requirements based on growth performance of White Pekin ducks for 21 days after hatch.J Anim Sci Technol. 2025 Mar;67(2):383-392. doi: 10.5187/jast.2024.e25. Epub 2025 Mar 31. J Anim Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 40264529 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing broiler growth performance through balanced net energy, standard ileal digestible lysine, and amylose/amylopectin ratios: a Box-Behnken response surface approach.Poult Sci. 2025 Aug;104(8):105287. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105287. Epub 2025 May 10. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40398308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoac International . 18th ed. Association of Official Analytical Chemist International; Gaithersburg, MD, USA: 2006. Official methods of analysis.
-
- Baker D.H. Problems and pitfalls in animal experiments designed to establish dietary requirements for essential nutrients. J Nutr. 1986;116:2339–2349. - PubMed
-
- Bernal L.E.P., Tavernari F.C., Rostagno H.S., Albino L.F.T. Digestible lysine requirements of broilers. Rev Bras Ciência Avícola. 2014;16:49–54.
-
- Berri C., Le Bihan-Duval E., Debut M., Sante-Lhoutellier V., Baeza E., Gigaud V., Jego Y., Duclos M.J. Consequence of muscle hypertrophy on characteristics of Pectoralis major muscle and breast meat quality of broiler chickens. J Anim Sci. 2007;85:2005–2011. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

