Molecular Epidemiology of Group B Streptococcus Isolates from Pregnant Women with Premature Rupture of Membranes in Fuzhou, China
- PMID: 36683909
- PMCID: PMC9849789
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S393935
Molecular Epidemiology of Group B Streptococcus Isolates from Pregnant Women with Premature Rupture of Membranes in Fuzhou, China
Abstract
Objective: This study investigated the molecular epidemiology of Group B Streptococcus (GBS) in pregnant women with premature rupture of membranes (PROM) in Fuzhou region of China as a source of clinical reference.
Methods: GBS isolates were obtained from pregnant women with PROM. All isolates were genotyped, serotyped, and tested for drug-resistance and virulence genes using PCR and DNA sequencing. Antibiotic susceptibility testing was performed using the Vitek® 2 automated system.
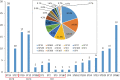
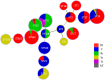
Results: Among the 140 GBS isolates, seventeen sequence types (STs) were identified, of which ST19 (20.0%) was the most prevalent, followed by ST862, ST10, and ST12. Three clonal complexes (CC19, CC10 and CC1) were identified. The predominant serotype was III (45.7%), followed by V (23.6%), Ib (18.6%), Ia (7.1%), and II (3.6%). The prevalence of multidrug resistance was 72.8% (102/140). All isolates were susceptible to penicillin G, ampicillin, quinupristin, linezolid, vancomycin, and tigecycline. The majority of isolates were resistant to erythromycin (70.0%), clindamycin (72.1%), and tetracycline (81.4%), and 28.6% of isolates were resistant to levofloxacin and moxifloxacin. Of the 98 erythromycin-resistant strains, mreA, ermB, mefA, mefE, ermA, and ermTR were detected in 100%, 70.4%, 49.0%, 22.4%, 13.3%, and 9.2%, respectively. No linB was detected among 101 clindamycin-resistant strains. Of the 114 tetracycline-resistant strains, tetM, tetK, tetL and tetO were detected in 52.6%, 61.4%, 7.9%, and 23.7%, respectively. Regarding virulence genes, all strains carried rib and hylB, followed by scpB (98.6%), and bca (80.7%), whereas only one strain carried bac.
Conclusion: ST19/III and ST862/III were the most prevalent GBS subtypes. Penicillin G remains a first-line antibiotic for intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis and treatment of GBS infections. The prevalence of resistance to clindamycin, erythromycin, and tetracycline is high among GBS isolates in the Fuzhou region. ST862 and ST651 are emerging animal origin STs in human infections, and may become potential zoonotic threats.
Keywords: China; Group B Streptococcus; antibiotic resistance; molecular epidemiology; premature rupture of the membranes.
© 2023 Liang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular characteristics of group B Streptococcus isolates from infants in southern mainland China.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Sep 18;19(1):812. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4434-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31533652 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus agalactiae in Brazil: serotype distribution, virulence determinants and antimicrobial susceptibility.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Jun 12;14:323. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-323. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24919844 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of virulence factors and antibiotic resistance genes in group B streptococcus from clinical samples.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Jan 28;21(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-05820-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33509097 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of virulence factors, antimicrobial resistance pattern and clonal complexes of group B streptococci isolated from neonates.Microb Pathog. 2016 Oct;99:119-122. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.08.016. Epub 2016 Aug 20. Microb Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27554272
-
Phenotypic and genetic differences among group B Streptococcus recovered from neonates and pregnant women in Shenzhen, China: 8-year study.BMC Microbiol. 2019 Aug 8;19(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1551-2. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31395013 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CAMP-negative Streptococcus agalactiae strains exhibited complete or partial chromosomal deletions of the CAMP-factor encoding gene cfb.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Apr 9;13(5):e0325724. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03257-24. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40202309 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic profiling of Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Streptococcus) isolates from pregnant women in northeastern Mexico: clonal complexes, virulence factors, and antibiotic resistance.PeerJ. 2025 May 22;13:e19454. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19454. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40416609 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype Distribution and High-Risk Factors Analysis of Group B Streptococcus in Late-Stage Pregnant Women in the Linyi Region.Int J Microbiol. 2024 Dec 19;2024:9910073. doi: 10.1155/ijm/9910073. eCollection 2024. Int J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39735411 Free PMC article.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous