Histone deacetylase inhibitors mitigate antipsychotic risperidone-induced motor side effects in aged mice and in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 36684015
- PMCID: PMC9852991
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1020831
Histone deacetylase inhibitors mitigate antipsychotic risperidone-induced motor side effects in aged mice and in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
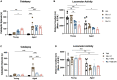
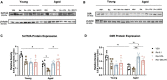
Antipsychotic drugs are still widely prescribed to control various severe neuropsychiatric symptoms in the elderly and dementia patients although they are off-label use in the United States. However, clinical practice shows greater side effects and lower efficacy of antipsychotics for this vulnerable population and the mechanisms surrounding this aged-related sensitivity are not well understood. Our previous studies have shown that aging-induced epigenetic alterations may be involved in the increasing severity of typical antipsychotic haloperidol induced side effects in aged mice. Still, it is unknown if similar epigenetic mechanisms extend to atypical antipsychotics, which are most often prescribed to dementia patients combined with severe neuropsychiatric symptoms. In this study, we report that atypical antipsychotic risperidone also causes increased motor side effect behaviors in aged mice and 5xFAD mice. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor Valproic Acid and Entinostat can mitigate the risperidone induced motor side effects. We further showed besides D2R, reduced expression of 5-HT2A, one of the primary atypical antipsychotic targets in the striatum of aged mice that are also mitigated by HDAC inhibitors. Finally, we demonstrate that specific histone acetylation mark H3K27 is hypoacetylated at the 5htr2a and Drd2 promoters in aged mice and can be reversed with HDAC inhibitors. Our work here establishes evidence for a mechanism where aging reduces expression of 5-HT2A and D2R, the key atypical antipsychotic drug targets through epigenetic alteration. HDAC inhibitors can restore 5-HT2A and D2R expression in aged mice and decrease the motor side effects in aged and 5xFAD mice.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; HDAC inhibitors; aging; antipsychotics; epigenetic; motor side effects; neuropsychiatric symptoms; risperidone.
Copyright © 2023 Rodriguez, Fisher, McClarty, Montalvo-Ortiz, Cui, Chan and Dong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
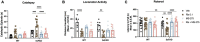
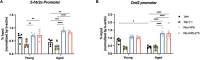
Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors reverse age-related increases in side effects of haloperidol in mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Aug;234(16):2385-2398. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4629-2. Epub 2017 Apr 18. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28421257 Free PMC article.
-
Dose Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Tacedinaline (CI-994) on Antipsychotic Haloperidol-Induced Motor and Memory Side Effects in Aged Mice.Front Neurosci. 2021 Oct 6;15:674745. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.674745. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34690667 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase 1 regulates haloperidol-induced motor side effects in aged mice.Behav Brain Res. 2023 Jun 5;447:114420. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114420. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Behav Brain Res. 2023. PMID: 37028517 Free PMC article.
-
[Antipsychotics in bipolar disorders].Encephale. 2004 Sep-Oct;30(5):417-24. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95456-5. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15627046 Review. French.
-
[Epigenetic mechanisms and alcohol use disorders: a potential therapeutic target].Biol Aujourdhui. 2017;211(1):83-91. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2017014. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Biol Aujourdhui. 2017. PMID: 28682229 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Distinguishing features of depression in dementia from primary psychiatric disease.Discov Ment Health. 2024 Jan 4;4(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s44192-023-00057-y. Discov Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 38175420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric acute-onset neuropsychiatric syndrome and pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorder associated with streptococcal infections: a delphi study and consensus document about definition, diagnostic criteria, treatment and follow-up.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 24;15:1420663. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1420663. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39512340 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation and histone modifications associated with antipsychotic treatment: a systematic review.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jan;30(1):296-309. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02735-x. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39227433
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

