Neuroprotective activity of a virus-safe nanofiltered human platelet lysate depleted of extracellular vesicles in Parkinson's disease and traumatic brain injury models
- PMID: 36684076
- PMCID: PMC9842020
- DOI: 10.1002/btm2.10360
Neuroprotective activity of a virus-safe nanofiltered human platelet lysate depleted of extracellular vesicles in Parkinson's disease and traumatic brain injury models
Abstract
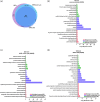
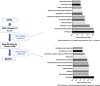
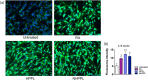
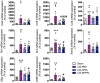
Brain administration of human platelet lysates (HPL) is a potential emerging biotherapy of neurodegenerative and traumatic diseases of the central nervous system. HPLs being prepared from pooled platelet concentrates, thereby increasing viral risks, manufacturing processes should incorporate robust virus-reduction treatments. We evaluated a 19 ± 2-nm virus removal nanofiltration process using hydrophilic regenerated cellulose hollow fibers on the properties of a neuroprotective heat-treated HPL (HPPL). Spiking experiments demonstrated >5.30 log removal of 20-22-nm non-enveloped minute virus of mice-mock particles using an immuno-quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay. The nanofiltered HPPL (NHPPL) contained a range of neurotrophic factors like HPPL. There was >2 log removal of extracellular vesicles (EVs), associated with decreased expression of pro-thrombogenic phosphatidylserine and procoagulant activity. LC-MS/MS proteomics showed that ca. 80% of HPPL proteins, including neurotrophins, cytokines, and antioxidants, were still found in NHPPL, whereas proteins associated with some infections and cancer-associated pathways, pro-coagulation and EVs, were removed. NHPPL maintained intact neuroprotective activity in Lund human mesencephalic dopaminergic neuron model of Parkinson's disease (PD), stimulated the differentiation of SH-SY5Y neuronal cells and showed preserved anti-inflammatory function upon intranasal administration in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury (TBI). Therefore, nanofiltration of HPL is feasible, lowers the viral, prothrombotic and procoagulant risks, and preserves the neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties in neuronal pre-clinical models of PD and TBI.
Keywords: human platelet lysate; nanofiltration; neuroprotection; prion; virus.
© 2022 The Authors. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Conflict of interest statement
Naoto Watanabe and Masayasu Takahara are employees of Asahi Kasei Medical. Thierry Burnouf and David Devos are named as inventors of patent applications owned by their respective universities and institutions and are founders of Invenis Biotherapies. The other authors have no commercial, proprietary, or financial interest in the products or companies described in this article.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

