A high-throughput biomimetic bone-on-a-chip platform with artificial intelligence-assisted image analysis for osteoporosis drug testing
- PMID: 36684077
- PMCID: PMC9842054
- DOI: 10.1002/btm2.10313
A high-throughput biomimetic bone-on-a-chip platform with artificial intelligence-assisted image analysis for osteoporosis drug testing
Abstract
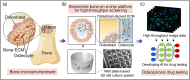
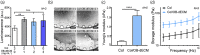
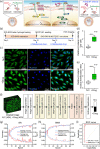
Although numerous organ-on-a-chips have been developed, bone-on-a-chip platforms have rarely been reported because of the high complexity of the bone microenvironment. With an increase in the elderly population, a high-risk group for bone-related diseases such as osteoporosis, it is essential to develop a precise bone-mimicking model for efficient drug screening and accurate evaluation in preclinical studies. Here, we developed a high-throughput biomimetic bone-on-a-chip platform combined with an artificial intelligence (AI)-based image analysis system. To recapitulate the key aspects of natural bone microenvironment, mouse osteocytes (IDG-SW3) and osteoblasts (MC3T3-E1) were cocultured within the osteoblast-derived decellularized extracellular matrix (OB-dECM) built in a well plate-based three-dimensional gel unit. This platform spatiotemporally and configurationally mimics the characteristics of the structural bone unit, known as the osteon. Combinations of native and bioactive ingredients obtained from the OB-dECM and coculture of two types of bone cells synergistically enhanced osteogenic functions such as osteocyte differentiation and osteoblast maturation. This platform provides a uniform and transparent imaging window that facilitates the observation of cell-cell interactions and features high-throughput bone units in a well plate that is compatible with a high-content screening system, enabling fast and easy drug tests. The drug efficacy of anti-SOST antibody, which is a newly developed osteoporosis drug for bone formation, was tested via β-catenin translocation analysis, and the performance of the platform was evaluated using AI-based deep learning analysis. This platform could be a cutting-edge translational tool for bone-related diseases and an efficient alternative to bone models for the development of promising drugs.
Keywords: bone formation; bone‐on‐a‐chip; deep learning; drug testing; high‐throughput analysis; osteoporosis.
© 2022 The Authors. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Porter JR, Ruckh TT, Popat KC. Bone tissue engineering: a review in bone biomimetics and drug delivery strategies. Biotechnol Prog. 2009;25(6):1539‐1560. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

