Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease therapies in the clinic
- PMID: 36684083
- PMCID: PMC9842041
- DOI: 10.1002/btm2.10367
Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease therapies in the clinic
Abstract
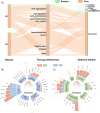
Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) are the most prevalent neurodegenerative diseases, affecting millions and costing billions each year in the United States alone. Despite tremendous progress in developing therapeutics that manage the symptoms of these two diseases, the scientific community has yet to develop a treatment that effectively slows down, inhibits, or cures neurodegeneration. To gain a better understanding of the current therapeutic frontier for the treatment of AD and PD, we provide a review on past and present therapeutic strategies for these two major neurodegenerative disorders in the clinical trial process. We briefly recap currently US Food and Drug Administration-approved therapies, and then explore trends in clinical trials across the variables of therapy mechanism of disease intervention, administration route, use of delivery vehicle, and outcome measures, across the clinical phases over time for "Drug" and "Biologic" therapeutics. We then present the success rate of past clinical trials and analyze the intersections in therapeutic approaches for AD and PD, revealing the shift in clinical trials away from therapies targeting neurotransmitter systems that provide symptomatic relief, and towards anti-aggregation, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, and regeneration strategies that aim to inhibit the root causes of disease progression. We also highlight the evolving distribution of the types of "Biologic" therapies investigated, and the slowly increasing yet still severe under-utilization of delivery vehicles for AD and PD therapeutics. We then briefly discuss novel preclinical strategies for treating AD and PD. Overall, this review aims to provide a succinct overview of the clinical landscape of AD and PD therapies to better understand the field's therapeutic strategy in the past and the field's evolution in approach to the present, to better inform how to effectively treat AD and PD in the future.
Keywords: Alzheimer's Disease; clinical trials; drug administration routes; outcome measures; therapy mechanisms; Parkinson's Disease; delivery vehicles.
© 2022 The Authors. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Alzheimer's Association et al. 2010 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2010;6(2):158‐194. - PubMed
-
- Wong W. Economic burden of Alzheimer disease and managed care considerations. Am J Manag Care. 2020;26(8 Suppl):S177‐S183. - PubMed
-
- Rocca WA. The burden of Parkinson's disease: a worldwide perspective. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(11):928‐929. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

