Patient-reported usability and satisfaction with electronic medication event reminder and monitor device for tuberculosis: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 36684395
- PMCID: PMC9853306
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101820
Patient-reported usability and satisfaction with electronic medication event reminder and monitor device for tuberculosis: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The success of a tuberculosis digital adherence technology relies on patients' satisfaction with and the usability of the technology. This study aimed to evaluate treatment satisfaction and usability of a digital medication event reminder and monitor (MERM) device for patients with tuberculosis to address the prespecified secondary endpoint of the SELFTB trial.
Methods: In this multicenter, randomised controlled trial, adults (≥18 years) with new or previously treated, bacteriologically-confirmed, drug-sensitive pulmonary tuberculosis who were eligible to start anti-tuberculosis therapy were recruited from 10 healthcare facilities in Ethiopia. With a computer-generated random number sequence, participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive a 15-day tuberculosis medication supply dispensed with an evriMED500® MERM device to self-administer and return every 15 days or the standard in-person DOT. Both arms were followed throughout the standard two-month intensive treatment phase. Treatment was based on the WHO-recommended two-month fixed-dose-combination of first-line anti-tuberculosis drug delivered as a single daily dose (2RHZE). Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire for Medication version 4 (TSQM 1.4©) was used to measure and compare treatment satisfaction between arms. Adapted System Usability Scale (SUS) was used to assess the usability of the device, with emphasis on ease of use, challenges, benefits, motivation, popularity, and recommendation. The findings were correlated with adherence and clinical endpoints including sputum smear conversion and IsoScreen urine isoniazid test results. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04216420.
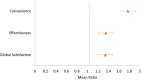
Findings: Between June 2, 2020, and June 15, 2021, 337 patients were screened for eligibility, of whom 109 participants enrolled and completed the satisfaction [control (n = 57) and intervention (n = 52) arms] and usability [intervention arm (n = 52)] questionnaires. TSQM 1.4© geometric mean scores were: Effectiveness 73.25 [geometric standard deviation (GSD) 1.28], Side Effects 100, Convenience 63.31 (GSD 1.45), and Global Satisfaction 77.29 (GSD 1.25). TSQM score was significantly higher in the intervention vs the control: Effectiveness [85.78 vs 63.43, 95% CI 1.35 (1.26-1.45), p < 0.001], Convenience [85.41 vs 48.18, 95% CI 1.77 (1.63-1.93), p < 0.001], and Global Satisfaction [90.19 vs 67.11, 95% CI 1.34 (1.26-1.43), p < 0.001]. There were significant associations between Global Satisfaction and medication adherence (p = 0.017). Average SUS score was 97.45%, which was close to the best imaginable SUS value of 100%. Likelihood to Recommend (LTR) value was ≥9, on a scale of 0-10, for 90.4% of MERM users, yielding higher net promoters. There was no significant association between usability and medication adherence (p = 0.691).
Interpretation: Our findings suggested that treatment satisfaction scores were superior in the intervention vs control arms and across the domains of Effectiveness, Convenience, and Global Satisfaction. There was excellent usability of the MERM device and a significantly higher number of users likely to promote the device. High tuberculosis burden countries may transform patient-centered care through ongoing evaluation and scale-up of digital health innovations.
Funding: U.S. National Institute of Health (NIH) Fogarty International Center and National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (D43 TW009127) and the Emory Center for AIDS Research (P30 AI050409).
Keywords: Digital adherence technology; Ethiopia; Medication events reminder and monitor; Patient-centered care; Satisfaction; Tuberculosis; Usability.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
V.C.M. has received investigator-initiated research grants (to the institution) and consultation fees (both unrelated to the current work) from Eli Lilly, Bayer, Gilead Sciences, and ViiV. All other authors report no potential conflicts.
Figures

References
-
- Cruz Rivera S., Aiyegbusi O.L., Ives J., et al. Ethical considerations for the inclusion of patient-reported outcomes in clinical research: the PRO Ethics guidelines. JAMA. 2022;327(19):1910–1919. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman M.A., Rappaport J., Seidman E. Springer US; Boston, MA: 2000. Empowerment theory: psychological, organizational and community levels of analysis. Handbook of Community Psychology; pp. 43–63.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) World Health Organization; Geneva: 2022. Global tuberculosis report 2022.https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240061729 Available at:
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

