Impact of Diabetes on Patient Outcomes in Breast Cancer Patients
- PMID: 36684403
- PMCID: PMC9851070
- DOI: 10.1159/000524513
Impact of Diabetes on Patient Outcomes in Breast Cancer Patients
Abstract
Background: Diabetes and the etiology of breast cancer are clearly associated. However, the impact of diabetes on prognosis is not yet understood. Therefore, we conducted a retrospective cohort study to examine the relationship between diabetes and patient outcomes in breast cancer patients.
Methods: We investigated 332 Japanese women with breast cancer who underwent curative surgery at our hospital. Patients without sufficient clinical information including hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and those with an observation period of less than 1 year were excluded.
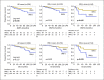
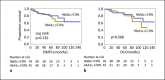
Results: Among the patients examined, 106 had diabetes at the time of their breast cancer diagnosis. Among the 296 patients with invasive breast carcinoma, 36 patients developed distant metastases during the mean observation period of 45 months. Sixteen patients died due to breast cancer, while 13 died of other causes. Multivariate analysis revealed that diabetes, tumor size, and estrogen receptor (ER) status were independent factors related to distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) (p = 0.038, p < 0.001, and p = 0.006, respectively). Kaplan-Meier curve analysis revealed that diabetes negatively affected the outcomes of ER-negative breast cancer patients both in DMFS and overall survival (p = 0.045 and p = 0.029, respectively). Meanwhile, patient outcomes did not differ according to the level of HbA1c in diabetes patients.
Conclusion: Patients with diabetes had a significantly shorter DMFS, and the negative effect of diabetes on patient outcomes was more evident in ER-negative breast cancer. Our data indicates the importance of primary prevention of diabetes for breast cancer patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Diabetes; Glycemic control; Insulin resistance; Prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 by The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Inoue M, Iwasaki M, Otani T, Sasazuki S, Noda M, Tsugane S. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of cancer: results from a Large-Scale Population-Based Cohort Study in Japan. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1871–1877. - PubMed
-
- Hardefeldt PJ, Edirimanne S, Eslick GD. Diabetes increases the risk of breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2012;19:793–803. - PubMed
-
- Liao S, Li J, Wei W, Wang L, Zhang Y, Li J, et al. Association between diabetes mellitus and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis of the literature. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12:1061–1065. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

