ADAR RNA editing on antisense RNAs results in apparent U-to-C base changes on overlapping sense transcripts
- PMID: 36684421
- PMCID: PMC9852825
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1080626
ADAR RNA editing on antisense RNAs results in apparent U-to-C base changes on overlapping sense transcripts
Abstract
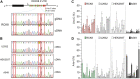
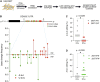
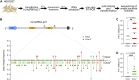
Despite hundreds of RNA modifications described to date, only RNA editing results in a change in the nucleotide sequence of RNA molecules compared to the genome. In mammals, two kinds of RNA editing have been described so far, adenosine to inosine (A-to-I) and cytidine to uridine (C-to-U) editing. Recent improvements in RNA sequencing technologies have led to the discovery of a continuously growing number of editing sites. These methods are powerful but not error-free, making routine validation of newly-described editing sites necessary. During one of these validations on DDX58 mRNA, along with A-to-I RNA editing sites, we encountered putative U-to-C editing. These U-to-C edits were present in several cell lines and appeared regulated in response to specific environmental stimuli. The same findings were also observed for the human long intergenic non-coding RNA p21 (hLincRNA-p21). A more in-depth analysis revealed that putative U-to-C edits result from A-to-I editing on overlapping antisense RNAs that are transcribed from the same loci. Such editing events, occurring on overlapping genes transcribed in opposite directions, have recently been demonstrated to be immunogenic and have been linked with autoimmune and immune-related diseases. Our findings, also confirmed by deep transcriptome data, demonstrate that such loci can be recognized simply through the presence of A-to-I and U-to-C mismatches within the same locus, reflective A-to-I editing both in the sense-oriented transcript and in the cis-natural antisense transcript (cis-NAT), implying that such clusters could be a mark of functionally relevant ADAR1 editing events.
Keywords: ADAR; DDX58/RIG-I; LINC-P21; MultiEditR; RNA editing; U-to-C.
Copyright © 2023 Pecori, Chillón, Lo Giudice, Arnold, Wüst, Binder, Marcia, Picardi and Papavasiliou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Crosslinking of base-modified RNAs by synthetic DYW-KP base editors implicates an enzymatic lysine as the nitrogen donor for U-to-C RNA editing.J Biol Chem. 2024 Aug;300(8):107454. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107454. Epub 2024 Jun 7. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38852885 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding regions of C. elegans mRNA undergo selective adenosine to inosine deamination and contain a small number of editing sites per transcript.RNA Biol. 2015;12(2):162-74. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1017220. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 25826568 Free PMC article.
-
A-to-I editing of Malacoherpesviridae RNAs supports the antiviral role of ADAR1 in mollusks.BMC Evol Biol. 2019 Jul 23;19(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12862-019-1472-6. BMC Evol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31337330 Free PMC article.
-
To edit or not to edit: regulation of ADAR editing specificity and efficiency.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Jan-Feb;7(1):113-27. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1319. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 26612708 Review.
-
ADAR RNA editing in innate immune response phasing, in circadian clocks and in sleep.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019 Mar;1862(3):356-369. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2018.10.011. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019. PMID: 30391332 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Mapping of Human dsRNAome Reveals Conservation, Neuronal Enrichment, and Intermolecular Interactions.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 27:2025.01.24.634786. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.24.634786. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39975386 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Genomic Landscape and Regulation of RNA Editing in Pekin Ducks Susceptible to Duck Hepatitis A Virus Genotype 3 Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 27;25(19):10413. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910413. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408741 Free PMC article.
-
Genome editing and kidney health.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Apr 17;17(5):sfae119. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae119. eCollection 2024 May. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 38766272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LoDEI: a robust and sensitive tool to detect transcriptome-wide differential A-to-I editing in RNA-seq data.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 23;15(1):9121. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53298-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39443485 Free PMC article.
-
REDInet: a temporal convolutional network-based classifier for A-to-I RNA editing detection harnessing million known events.Brief Bioinform. 2025 Mar 4;26(2):bbaf107. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaf107. Brief Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40112338 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

