Interplay between integrins and cadherins to control bone differentiation upon BMP-2 stimulation
- PMID: 36684447
- PMCID: PMC9846056
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1027334
Interplay between integrins and cadherins to control bone differentiation upon BMP-2 stimulation
Abstract
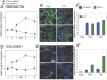
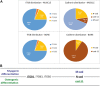
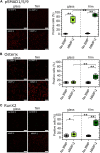
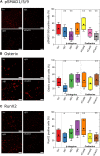
Introduction: Upon BMP-2 stimulation, the osteoblastic lineage commitment in C2C12 myoblasts is associated with a microenvironmental change that occurs over several days. How does BMP-2 operate a switch in adhesive machinery to adapt to the new microenvironment and to drive bone cell fate is not well understood. Here, we addressed this question for BMP-2 delivered either in solution or physically bound of a biomimetic film, to mimic its presentation to cells via the extracellular matrix (ECM). Methods: Biommetics films were prepared using a recently developed automated method that enable high content studies of cellular processes. Comparative gene expressions were done using RNA sequencing from the encyclopedia of the regulatory elements (ENCODE). Gene expressions of transcription factors, beta chain (1, 3, 5) integrins and cadherins (M, N, and Cad11) were studied using quantitative PCR. ECM proteins and adhesion receptor expressions were also quantified by Western blots and dot blots. Their spatial organization in and around cells was studied using immuno-stainings. The individual effect of each receptor on osteogenic transcription factors and alkaline phosphatase expression were studied using silencing RNA of each integrin and cadherin receptor. The organization of fibronectin was studied using immuno-staining and quantitative microscopic analysis. Results: Our findings highlight a switch of integrin and cadherin expression during muscle to bone transdifferentiation upon BMP-2 stimulation. This switch occurs no matter the presentation mode, for BMP-2 presented in solution or via the biomimetic film. While C2C12 muscle cells express M-cadherin and Laminin-specific integrins, the BMP-2-induced transdifferentiation into bone cells is associated with an increase in the expression of cadherin-11 and collagen-specific integrins. Biomimetic films presenting matrix-bound BMP-2 enable the revelation of specific roles of the adhesive receptors depending on the transcription factor. Discussion: While β3 integrin and cadherin-11 work in concert to control early pSMAD1,5,9 signaling, β1 integrin and Cadherin-11 control RunX2, ALP activity and fibronectin organization around the cells. In contrast, while β1 integrin is also important for osterix transcriptional activity, Cadherin-11 and β5 integrin act as negative osterix regulators. In addition, β5 integrin negatively regulates RunX2. Our results show that biomimetic films can be used to delinate the specific events associated with BMP-2-mediated muscle to bone transdifferentiation. Our study reveals how integrins and cadherins work together, while exerting distinct functions to drive osteogenic programming. Different sets of integrins and cadherins have complementary mechanical roles during the time window of this transdifferentiation.
Keywords: BMP-2 (bone morphogenetic protein-2); adhesion receptors; cadherins; extracellular matrix (ECM); integrins; osteoblast differentation.
Copyright © 2023 Valat, Fourel, Sales, Machillot, Bouin, Fournier, Bosc, Arboléas, Bourrin-Reynard, Wagoner Johnson, Bruckert, Albigès-Rizo and Picart.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mechanism of BMP-2 stimulated adhesion of osteoblastic cells to titanium alloy.Biol Cell. 1999 Mar;91(2):131-42. doi: 10.1016/s0248-4900(99)80037-9. Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10399828
-
Collagen integrin receptors regulate early osteoblast differentiation induced by BMP-2.J Bone Miner Res. 1999 Jul;14(7):1075-83. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.7.1075. J Bone Miner Res. 1999. PMID: 10404007
-
Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from dental bud: Role of integrins and cadherins.Stem Cell Res. 2015 Nov;15(3):618-628. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2015.09.011. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Stem Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 26513557
-
Integrin and cadherin signaling in bone: role and potential therapeutic targets.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Nov;25(11):567-75. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 25034128 Review.
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
Cited by
-
Insight into the role of integrins and integrins-targeting biomaterials in bone regeneration.Connect Tissue Res. 2024 Sep;65(5):343-363. doi: 10.1080/03008207.2024.2396002. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Connect Tissue Res. 2024. PMID: 39297793 Review.
-
Integrated bulk RNA and single-cell analysis with experimental validation reveal oxidative stress-related diagnostic biomarkers for osteoporosis.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 29;20(4):e0322326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322326. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40299834 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of VE-cadherin in regulating endothelial cell behaviour during angiogenesis.Front Physiol. 2023 Aug 2;14:1234104. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1234104. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37601629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Developments in Layer-by-Layer Assembly for Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering Applications.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Mar;13(8):e2302713. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202302713. Epub 2024 Jan 7. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38116714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

