Immunosuppressive functions of melanoma cell-derived exosomes in plasma of melanoma patients
- PMID: 36684448
- PMCID: PMC9853022
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1080925
Immunosuppressive functions of melanoma cell-derived exosomes in plasma of melanoma patients
Abstract
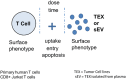
Tumor-derived exosomes (TEX) are a subset of small extracellular vesicles (sEV) present in all body fluids of patients with cancer. In plasma of patients with metastatic melanoma, numbers of exosomes produced by melanoma cells called MTEX are elevated. To study the role of MTEX in melanoma progression, immunoaffinity-based separation of MTEX from total plasma exosomes was performed. The surface of MTEX was decorated by various checkpoint inhibitory proteins, and upon coincubation with immune recipient cells, MTEX suppressed anti-tumor functions of these cells. MTEX emerge as a major mechanism of immune suppression in melanoma and thus might play a role in promoting melanoma progression.
Keywords: exosomes; immune capture; immune suppression; melanoma; melanoma cell-derived exosomes (MTEX); small extracellular vesicles.
Copyright © 2023 Whiteside.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunoaffinity-based isolation of melanoma cell-derived exosomes from plasma of patients with melanoma.J Extracell Vesicles. 2018 Feb 15;7(1):1435138. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1435138. eCollection 2018. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018. PMID: 29511460 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoaffinity-Based Isolation of Melanoma Cell-Derived and T Cell-Derived Exosomes from Plasma of Melanoma Patients.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2265:305-321. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1205-7_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33704724 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling of Tumor-Derived sEV Impacts Melanoma Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 17;21(14):5066. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145066. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32709086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melanoma cell-derived exosomes in plasma of melanoma patients suppress functions of immune effector cells.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 9;10(1):92. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56542-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31919420 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-Derived Exosomes (TEX) and Their Role in Immuno-Oncology.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 9;22(12):6234. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126234. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34207762 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic features of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles: challenges and opportunities.Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2024 Aug 27;5(3):455-470. doi: 10.20517/evcna.2024.12. eCollection 2024. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2024. PMID: 39697624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes as key mediators in immune and cancer cell interactions: insights in melanoma progression and therapy.Arch Dermatol Res. 2025 Apr 19;317(1):729. doi: 10.1007/s00403-025-04237-4. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025. PMID: 40252131 Review.
-
Cutaneous Melanoma: A Review of Multifactorial Pathogenesis, Immunohistochemistry, and Emerging Biomarkers for Early Detection and Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 1;24(21):15881. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115881. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biology of extracellular vesicles and the potential of tumor-derived vesicles for subverting immunotherapy of cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Jan 23;13(1):e010376. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010376. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39855711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different origin-derived exosomes and their clinical advantages in cancer therapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 27;15:1401852. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1401852. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38994350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amor Lopez A., Mazariegos M. S., Capuano A., Ximenez-Embun P., Hergueta-Redondo M., Recio J. A., et al. (2021). Inactivation of EMILIN-1 by proteolysis and secretion in small extracellular vesicles favors melanoma progression and metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 7406. 10.3390/ijms22147406 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

