A study to evaluate the knowledge, vaccination status and acceptance of adult vaccinations against respiratory infections in patients with type 2 diabetes in South India
- PMID: 36684486
- PMCID: PMC9838543
- DOI: 10.1007/s13410-022-01166-0
A study to evaluate the knowledge, vaccination status and acceptance of adult vaccinations against respiratory infections in patients with type 2 diabetes in South India
Abstract
Introduction: Respiratory infections like influenza and pneumococcus increase mortality, morbidity, hospitalisation risks and healthcare costs in people with type 2 diabetes which can be prevented by vaccinations. However, there is not much data regarding how many people with type 2 diabetes in India receive pneumococcal and influenza vaccinations.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study conducted between March 2022 to May 2022 at a tertiary care centre in South India. Patients were interviewed through face to face questionnaire regarding awareness, knowledge of influenza and pneumococcal infections, availability and need of vaccines, vaccination status and the possible reasons for not receiving vaccines.
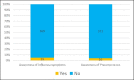
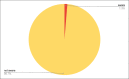
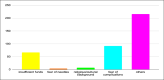
Results: A total of 388 patients were recruited in the study. Knowledge about influenza and pneumococcal infections were present only in 4.8% and 4.1% respectively. And 98.7% of patients had no awareness about the availability and need for vaccines. Only 0.5% and 0.7% of patients received influenza and pneumococcal vaccinations respectively. After counselling and spreading awareness, 76.2% of patients said that they would receive vaccination in the next visit. Also, 23.19% of the patients refused to take any vaccinations even after counselling. And 23.7% of patients feared complications after vaccinations.
Conclusion: Pneumococcal and Influenza vaccination uptake rates are extremely low in people with type 2 diabetes in India. Urgent measures are required to increase the awareness in patients and healthcare workers about the availability, need for vaccinations and effectiveness of vaccines which would lead to improvement in vaccination rates.
Keywords: Infections; Influenza; Pneumococcus; Type 2 diabetes; Vaccination.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Research Society for Study of Diabetes in India 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Figures
References
-
- Global health estimates 2020: deaths by cause, age, sex, by country and by region, 2000–2019. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources