KCNQ2 Encephalopathy and Responsiveness to Pyridoxal-5'-Phosphate
- PMID: 36684546
- PMCID: PMC9848766
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1721384
KCNQ2 Encephalopathy and Responsiveness to Pyridoxal-5'-Phosphate
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Erratum: KCNQ2 Encephalopathy and Responsiveness to Pyridoxal-5'-Phosphate.J Pediatr Genet. 2021 Oct 8;12(1):e1. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1735896. eCollection 2023 Mar. J Pediatr Genet. 2021. PMID: 36688947 Free PMC article.
Abstract
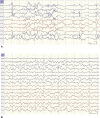
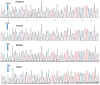
KCNQ2 mutations encompass a wide range of phenotypes, ranging from benign familial neonatal seizure to a clinical spectrum of early-onset epileptic encephalopathy that occurs in the early neonatal period. We report an infant with KCNQ2 encephalopathy presenting as neonatal seizure, initially controlled by two anticonvulsants. Electroencephalogram (EEG) showed repetitive multifocal epileptiform discharges, which remained similar after administration of intravenous pyridoxine injection. Seizure recurred at the age of 3 months preceded by an episode of minor viral infection, which occurred multiple times per day. No significant change in seizure frequency was observed after 5-day oral pyridoxine trial, but subsequently, there was dramatic seizure improvement with oral pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (PLP). We hope to alert clinicians that in patients with neonatal epileptic encephalopathy, particularly with known KCNQ2 mutations, intravenous injection of pyridoxine (preferably with EEG monitoring), followed by both oral trial of pyridoxine and PLP should be considered. KCNQ2 mutations should also be considered in vitamin B6-responsive patients.
Keywords: vitamin B 6 -responsive patients; KCNQ2 mutation; epileptic encephalopathy; neonatal seizure; pyridoxal-5′-phosphate; pyridoxine.
Thieme. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Nabbout R, Dulac O. Epilepsy. Genetics of early-onset epilepsy with encephalopathy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2012;8(03):129–130. - PubMed
-
- Kato M, Yamagata T, Kubota M. Clinical spectrum of early onset epileptic encephalopathies caused by KCNQ2 mutation . Epilepsia. 2013;54(07):1282–1287. - PubMed
-
- Miceli F, Soldovieri M V, Joshi N, Weckhuysen S, Cooper E, Taglialatela M. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; KCNQ2-related disorders. April 27, 2010 [Updated September 27, 2018] pp. 1993–2020. - PubMed
-
- Ohtahara S, Yamatogi Y, Ohtsuka Y. Vitamin B(6) treatment of intractable seizures. Brain Dev. 2011;33(09):783–789. - PubMed
-
- Saitsu H, Kato M, Koide A. Whole exome sequencing identifies KCNQ2 mutations in Ohtahara syndrome . Ann Neurol. 2012;72(02):298–300. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

