Jia-Wei-Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction modulates intestinal flora and metabolites in acute coronary syndrome model
- PMID: 36684592
- PMCID: PMC9845626
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1038273
Jia-Wei-Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction modulates intestinal flora and metabolites in acute coronary syndrome model
Abstract
Aims: We assessed the efficacy of the traditional Chinese medicine formulation Jia-Wei-Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction (HJ11) in the treatment of acute coronary syndrome and evaluated its impact on the intestinal microbiota and their metabolites.
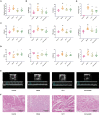
Methods: An acute coronary syndrome model was established in rats, which were randomly assigned to the model, HJ11 treatment, and atorvastatin treatment groups. Rats were then administered saline solution (model and sham operation control groups) or drugs by oral gavage for 28 d. Echocardiography was performed and serum creatine kinase-MB and cardiac troponin I levels were monitored to examine the cardiac function. Inflammation was evaluated using hematoxylin and eosin staining of heart tissue, and serum interleukin-2, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein measurements. Gut microbiota composition was analyzed via 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Metabolomics was used to determine fecal metabolites and elucidate the modes of action of HJ11 in acute coronary syndrome treatment.
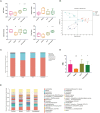
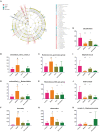
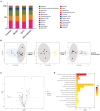
Results: HJ11 improved cardiac function and attenuated inflammation in rats with acute coronary syndrome. Relative to the untreated model group, the HJ11-treated group presented normalized Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio and reduced abundances of the bacterial genera norank_f__Ruminococcaceae, Desulfovibrio, Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1, Adlercreutzia, Staphylococcus, Bacteroides, Prevotella, Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, unclassified_o__Bacteroidales, and Ruminococcus_gauvreauii_group. We found 23 differentially expressed intestinal metabolites, and the enriched metabolic pathways were mainly related to amino acid metabolism. We also discovered that asymmetric dimethylarginine levels were strongly associated with cardiovascular disease. Correlation analyses revealed strong associations among intestinal microflora, their metabolites, proinflammatory factors, and cardiac function. Hence, the therapeutic effects of HJ11 on acute coronary syndrome are related to specific alterations in gut microbiota and their metabolites.
Conclusion: This work demonstrated that HJ11 effectively treats acute coronary syndrome. HJ11 seems to increase the abundance of beneficial bacterial taxa (Bacteroides and Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group), mitigate the risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease, alter bacterial metabolites, lower asymmetric dimethylarginine levels, and effectively treat acute coronary syndrome.
Keywords: ACS; Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction; TCM; gut flora; metabolomics.
Copyright © 2023 Zhao, Wang, Ma, Liang, Zhang, Gao, Dong, Bai and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction on myocardial I/R rats by regulating gut microbiota to inhibit LPS-induced TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Jun 2;23(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04013-9. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37268931 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated chemical composition, transcriptomics, and network pharmacology to reveal the mechanism of Jia-Wei-Si-Miao-Yong-An Decoction in ACS model rats.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:157027. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157027. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40645073
-
Efficacy and Mechanism of Qianshan Huoxue Gao in Acute Coronary Syndrome via Regulation of Intestinal Flora and Metabolites.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Feb 22;17:579-595. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S396649. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 36855515 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney-tonifying blood-activating decoction delays ventricular remodeling in rats with chronic heart failure by regulating gut microbiota and metabolites and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/p65 nuclear factor kappa-B/aquaporin-4 signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Aug 10;330:118110. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118110. Epub 2024 Apr 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38580189
-
HJ11 decoction restrains development of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing ACSL4-mediated ferroptosis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 22;13:1024292. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1024292. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36483736 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recent advances of traditional Chinese medicine against cardiovascular disease: overview and potential mechanisms.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 30;15:1366285. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1366285. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39403576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating 16S rRNA Sequencing, Microflora Metabolism, and Network Pharmacology to Investigate the Mechanism of SBL in Alleviating HDM-Induced Allergic Rhinitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 8;25(16):8655. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168655. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201342 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction on myocardial I/R rats by regulating gut microbiota to inhibit LPS-induced TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Jun 2;23(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04013-9. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37268931 Free PMC article.
-
Causal relationship between the gut microbiota, immune cells, and coronary heart disease: a mediated Mendelian randomization analysis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 5;15:1449935. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1449935. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39161605 Free PMC article.
-
Huayu Qutan formula can improve platelet aggregation in acute coronary syndrome rats by regulating gut microbes to drive trimethylamine/flavin containing monooxygenase 3/trimethylamine N-oxide pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2025 Aug;45(4):747-758. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.04.005. J Tradit Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40810220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Luca G, Verdoia M, Savonitto S, Piatti L, Grosseto D, Morici N, et al. Impact of diabetes on clinical outcome among elderly patients with acute coronary syndrome treated with percutaneous coronary intervention: insights from the ELDERLY ACS 2 trial. J Cardiovasc Med. (2021) 21:453–9. 10.2459/JCM.0000000000000978 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jingqing H. Analysis of the pathogenesis of coronary heart disease under the framework of the theory of pathogenesis and chemistry. Chinese Journal of Basic Chinese Medicine. (2017) 23:4–11.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

