Inter-rater and intra-rater reliability of isotonic exercise monitoring device for measuring active knee extension
- PMID: 36684676
- PMCID: PMC9851051
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.14672
Inter-rater and intra-rater reliability of isotonic exercise monitoring device for measuring active knee extension
Abstract
Background: The goal of this study was to assess the reliability of electromyography and range of motion measurements obtained using a knee exercise monitoring system. This device was developed to collect data on knee exercise activities.
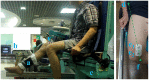
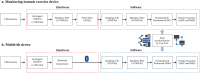
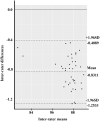
Methods: Twenty healthy individuals performed isotonic quadriceps exercises in this study. The vastus medialis surface electromyography (sEMG) and range of motion (ROM) of the knee were recorded during the exercise using the isotonic knee exercise monitoring device, the Mobi6-6b, and a video camera system. Each subject underwent a second measuring session at least 24 h after the first session. To determine reliability, the intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) and standard error of measurement (SEM) at the 95% confidence interval were calculated, and a Bland-Altman analysis was performed.
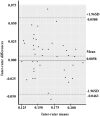
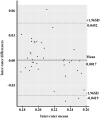
Results: For inter-rater reliability, the ICCs of the mean absolute value (MAV) and root mean square (RMS) of sEMG were 0.73 (0.49, 0.86) and 0.79 (0.61, 0.89), respectively. ROM had an ICC of 0.93 (0.02, 0.98). The intra-rater reliability of the MAV of the sEMG was 0.89 (0.71, 0.96) and the intra-rater reliability of RMS of the sEMG was 0.88 (0.70, 0.95). The ROM between days had an intra-rater reliability of 0.82 (0.54, 0.93). The Bland-Altman analysis demonstrated no systematic bias in the MAV and RMS of sEMG, but revealed a small, systematic bias in ROM (-0.8311 degrees).
Conclusion: For sEMG and range of motion measures, the isotonic knee exercise monitoring equipment revealed moderate to excellent inter- and intra-rater agreement. However, the confidence interval of ROM inter-rater reliability was quite large, indicating a small agreement bias; hence, the isotonic knee exercise monitor may not be suitable for measuring ROM. This isotonic knee exercise monitor could detect and collect information on a patient's exercise activity for the benefit of healthcare providers.
Keywords: Inter-rater reliability; Intra-rater reliability; Isotonic exercise device; Knee extension; Knee rehabilitation; Range of motion; Surface electromyography.
© 2023 Limsakul et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The iPhone Measure app level function as a measuring device for the weight bearing lunge test in adults: a reliability study.J Foot Ankle Res. 2019 Jul 9;12:37. doi: 10.1186/s13047-019-0347-9. eCollection 2019. J Foot Ankle Res. 2019. PMID: 31333763 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability of range of motion in straight leg raise and hip extension tests among healthy young adults using a smartphone application.J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2024 Oct;40:683-688. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2024.05.033. Epub 2024 May 29. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2024. PMID: 39593664
-
Inter-rater and intra-rater reliability of the fluid goniometer for measuring active knee flexion in painful knees; correlations do not mean agreement.J Phys Ther Sci. 2017 Jun;29(6):984-988. doi: 10.1589/jpts.29.984. Epub 2017 Jun 7. J Phys Ther Sci. 2017. PMID: 28626305 Free PMC article.
-
The reliability of video fluoroscopy, ultrasound imaging, magnetic resonance imaging and radiography for measurements of lumbar spine segmental range of motion in-vivo: A review.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023;36(1):117-135. doi: 10.3233/BMR-210285. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 35988213 Review.
-
Effects of Eccentric Resistance Training on Lower-Limb Passive Joint Range of Motion: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2023 Apr 1;55(4):710-721. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000003085. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2023. PMID: 36730587
References
-
- Boldrini P, Bernetti A, Fiore P, SIMFER Executive Committee, SIMFER Committee for International Affairs Impact of COVID-19 outbreak on rehabilitation services and Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine physicians’ activities in Italy. An official document of the Italian PRM society (SIMFER) European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine. 2020;56(3):316–318. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.20.06256-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bujang MA, Baharum N. A simplified guide to determination of sample size requirements for estimating the value of intraclass correlation coefficient: a review. Archives of Orofacial Sciences. 2017;12(1):1–11.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

