Root pruning improves maize water-use efficiency by root water absorption
- PMID: 36684736
- PMCID: PMC9845614
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1023088
Root pruning improves maize water-use efficiency by root water absorption
Abstract
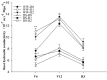
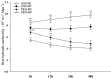
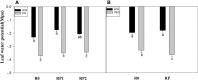
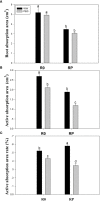
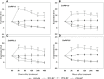
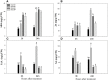
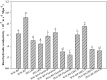
Root systems are an important component of plants that impact crop water-use efficiency (WUE) and yield. This study examined the effects of root pruning on maize yield, WUE, and water uptake under pot and hydroponic conditions. The pot experiment showed that root pruning significantly decreased root/shoot ratio. Both small root pruning (cut off about 1/5 of the root system, RP1) and large root pruning (cut off about 1/3 of the root system, RP2) improved WUE and root hydraulic conductivity (Lpr) in the residual root system. Compared with that in the un-cut control, at the jointing stage, RP1 and RP2 increased Lpr by 43.9% and 31.5% under well-watered conditions and 27.4% and 19.8% under drought stress, respectively. RP1 increased grain yield by 12.9% compared with that in the control under well-watered conditions, whereas both pruning treatments did not exhibit a significant effect on yield under drought stress. The hydroponic experiment demonstrated that root pruning did not reduce leaf water potential but increased residual root hydraulic conductivity by 26.2% at 48 h after root pruning under well-watered conditions. The foregoing responses may be explained by the upregulation of plasma membrane intrinsic protein gene and increases in abscisic acid and jasmonic acid in roots. Increased auxin and salicylic acid contributed to the compensated lateral root growth. In conclusion, root pruning improved WUE in maize by root water uptake.
Keywords: abscisic acid; jasmonic acid; leaf water potential; root hydraulic conductivity; root pruning.
Copyright © 2023 Yan, Zhang, Li, Zhang, Ren, Chen, Cai and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdelhakam S., Rabei S. H., Nada R. M., Abogadallah G. M. (2021). The complementary role of root and leaf PIP1 and PIP2 aquaporins drives the anisohydric behavior in Helinathus annuus L. Environ. Exp. Bot. 182, 104314. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104314 - DOI
-
- Adie B. A. T., Perez-Perez J. N., Perez-Perez M. M., Godoy M., Sanchez-Serrano J. J., Schmelz E. A., et al. (2007). ABA is an essential signal for plant resistance to pathogens affecting JA biosynthesis and the activation of defenses in arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 19, 1665–1681. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.048041 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aroca R. (2006). Exogenous catalase and ascorbate modify the effects of abscisic acid (ABA) on root hydraulic properties in Phaseolus vulgaris L. plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 25, 10–17. doi: 10.1007/s00344-005-0075-1 - DOI
-
- Aroca R., Vernieri P., Irigoyen J. J., Sanchez-Diaz M., Tognoni F., Pardossi A. (2003). Involvement of abscisic acid in leaf and root of maize (Zea mays L.) in avoiding chilling-induced water stress. Plant Sci. 165, 671–679. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9452(03)00257-7 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

