MePAL6 regulates lignin accumulation to shape cassava resistance against two-spotted spider mite
- PMID: 36684737
- PMCID: PMC9853075
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1067695
MePAL6 regulates lignin accumulation to shape cassava resistance against two-spotted spider mite
Abstract
Introduction: The two-spotted spider mite (TSSM) is a devastating pest of cassava production in China. Lignin is considered as an important defensive barrier against pests and diseases, several genes participate in lignin biosynthesis, however, how these genes modulate lignin accumulation in cassava and shape TSSM-resistance is largely unknown.
Methods: To fill this knowledge gap, while under TSSM infestation, the cassava lignin biosynthesis related genes were subjected to expression pattern analysis followed by family identification, and genes with significant induction were used for further function exploration.
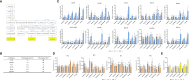
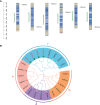
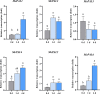
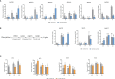
Results: Most genes involved in lignin biosynthesis were up-regulated when the mite-resistant cassava cultivars were infested by TSSM, noticeably, the MePAL gene presented the most vigorous induction among these genes. Therefore, we paid more attention to dissect the function of MePAL gene during cassava-TSSM interaction. Gene family identification showed that there are 6 MePAL members identified in cassava genome, further phylogenetic analysis, gene duplication, cis-elements and conserved motif prediction speculated that these genes may probably contribute to biotic stress responses in cassava. The transcription profile of the 6 MePAL genes in TSSM-resistant cassava cultivar SC9 indicated a universal up-regulation pattern. To further elucidate the potential correlation between MePAL expression and TSSM-resistance, the most strongly induced gene MePAL6 were silenced using virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) assay, we found that silencing of MePAL6 in SC9 not only simultaneously suppressed the expression of other lignin biosynthesis genes such as 4-coumarate--CoA ligase (4CL), hydroxycinnamoyltransferase (HCT) and cinnamoyl-CoA reductase (CCR), but also resulted in decrease of lignin content. Ultimately, the suppression of MePAL6 in SC9 can lead to significant deterioration of TSSM-resistance.
Discussion: This study accurately identified MePAL6 as critical genes in conferring cassava resistance to TSSM, which could be considered as promising marker gene for evaluating cassava resistance to insect pest.
Keywords: PAL gene family; VIGS; cassava; lignin biosynthesis; mite-resistance; two-spotted spider mite.
Copyright © 2023 Yao, Liang, Chen, Liu, Wu, Wu, Shui, Qiao, Zhang and Geng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Overexpression of leucoanthocyanidin reductase or anthocyanidin reductase elevates tannins content and confers cassava resistance to two-spotted spider mite.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 18;13:994866. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.994866. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36061805 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of cassava germplasms resistant to two-spotted spider mite in China: From greenhouse large-scale screening to field validation.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 7;13:1054909. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1054909. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36570903 Free PMC article.
-
Tomato Cultivars Resistant or Susceptible to Spider Mites Differ in Their Biosynthesis and Metabolic Profile of the Monoterpenoid Pathway.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Feb 26;12:630155. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.630155. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33719301 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-Herbivore Interactions: A Case of an Extreme Generalist, the Two-Spotted Spider Mite Tetranychus urticae.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2017 Dec;30(12):935-945. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-07-17-0168-CR. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2017. PMID: 28857675 Review.
-
Trends in lignin modification: a comprehensive analysis of the effects of genetic manipulations/mutations on lignification and vascular integrity.Phytochemistry. 2002 Oct;61(3):221-94. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(02)00211-x. Phytochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12359514 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of metabolomics and transcriptomics reveals the regulation mechanism of the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway in insect resistance traits in Solanum habrochaites.Hortic Res. 2024 Jan 9;11(2):uhad277. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhad277. eCollection 2024 Feb. Hortic Res. 2024. PMID: 38344649 Free PMC article.
-
The Key Role of Plant Hormone Signaling Transduction and Flavonoid Biosynthesis Pathways in the Response of Chinese Pine (Pinus tabuliformis) to Feeding Stimulation by Pine Caterpillar (Dendrolimus tabulaeformis).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 8;25(12):6354. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126354. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928063 Free PMC article.
-
Mite Infestation Induces a Moderate Oxidative Stress in Short-Term Soybean Exposure.Plants (Basel). 2025 Feb 14;14(4):590. doi: 10.3390/plants14040590. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006849 Free PMC article.
-
The MdERF61-mdm-miR397b-MdLAC7b module regulates apple resistance to Fusarium solani via lignin biosynthesis.Plant Physiol. 2024 Dec 23;197(1):kiae518. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiae518. Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39374536 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of the Gossypium hirsutum CAD gene family and functional study of GhiCAD23 under drought stress.PeerJ. 2024 Nov 29;12:e18439. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18439. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39624134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellotti A., Herrera Campo B. V., Hyman G. (2012). Cassava production and pest management: Present and potential threats in a changing environment. Trop. Plant Biol. 16, 39–72. doi: 10.1007/s12042-011-9091-4 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

