Application of chloroplast genome in the identification of Phyllanthus urinaria and its common adulterants
- PMID: 36684764
- PMCID: PMC9853280
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1099856
Application of chloroplast genome in the identification of Phyllanthus urinaria and its common adulterants
Abstract
Background: Phyllanthus urinaria L. is extensively used as ethnopharmacological material in China. In the local marketplace, this medicine can be accidentally contaminated, deliberately substituted, or mixed with other related species. The contaminants in herbal products are a threat to consumer safety. Due to the scarcity of genetic information on Phyllanthus plants, more molecular markers are needed to avoid misidentification.
Methods: In this study, the complete chloroplast genome of nine species of the genus Phyllanthus was de novo assembled and characterized.
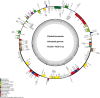
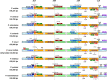
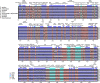
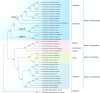
Results: This study revealed that all of these species exhibited a conserved quadripartite structure, which includes a large single copy (LSC) region and small single copy (SSC) region, and two copies of inverted repeat regions (IRa and IRb), which separate the LSC and SSC regions. And the genome structure, codon usage, and repeat sequences were highly conserved and showed similarities among the nine species. Three highly variable regions (trnS-GCU-trnG-UCC, trnT-UGU-trnL-UAA, and petA-psbJ) might be helpful as potential molecular markers for identifying P. urinaria and its contaminants. In addition, the molecular clock analysis results showed that the divergence time of the genus Phyllanthus might occur at ~ 48.72 Ma.
Conclusion: This study provides valuable information for further species identification, evolution, and phylogenetic research of Phyllanthus.
Keywords: Phyllanthus urinaria; chloroplast genome; molecular marker; phylogenetic; species identification.
Copyright © 2023 Fang, Dai, Liao, Zhou and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A review of Phyllanthus urinaria L. in the treatment of liver disease: viral hepatitis, liver fibrosis/cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 9;15:1443667. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1443667. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39185304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative analysis of medicinal plant Isodon rubescens and its common adulterants based on chloroplast genome sequencing.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 21;13:1036277. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1036277. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36479509 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Chloroplast Genome and New Insights Into Phylogenetic Relationships of Polygonatum and Tribe Polygonateae.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 24;13:882189. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.882189. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35812916 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic comparison of eight new plastome sequences from Ipomoea L.PeerJ. 2019 Mar 11;7:e6563. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6563. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30881765 Free PMC article.
-
A Review: Mechanism of Phyllanthus urinaria in Cancers-NF-κB, P13K/AKT, and MAPKs Signaling Activation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Aug 26;2021:4514342. doi: 10.1155/2021/4514342. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34484390 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analysis of Six Chloroplast Genomes in Chenopodium and Its Related Genera (Amaranthaceae): New Insights into Phylogenetic Relationships and the Development of Species-Specific Molecular Markers.Genes (Basel). 2023 Dec 6;14(12):2183. doi: 10.3390/genes14122183. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38137004 Free PMC article.
-
A review of Phyllanthus urinaria L. in the treatment of liver disease: viral hepatitis, liver fibrosis/cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 9;15:1443667. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1443667. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39185304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the complete chloroplast genome of Curcuma comosa and C. latifolia.Heliyon. 2024 May 15;10(10):e31248. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31248. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38813184 Free PMC article.
-
The complete chloroplast genome and phylogentic results support the species position of Swertia banzragczii and Swertia marginata (Gentianaceae) in Mongolia.Bot Stud. 2024 Apr 24;65(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40529-024-00417-z. Bot Stud. 2024. PMID: 38656420 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome and new insights into phylogenetic relationships of Ajuga and common adulterants.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Oct 25;14:1251829. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1251829. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37954994 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

