Maize-soybean intercropping at optimal N fertilization increases the N uptake, N yield and N use efficiency of maize crop by regulating the N assimilatory enzymes
- PMID: 36684768
- PMCID: PMC9846272
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1077948
Maize-soybean intercropping at optimal N fertilization increases the N uptake, N yield and N use efficiency of maize crop by regulating the N assimilatory enzymes
Abstract
Introduction: Surplus use of chemical nitrogen (N) fertilizers to increase agricultural Q9 production causes severe problems to the agricultural ecosystem and environment. This is contrary to N use efficiency and sustainable agricultural production.
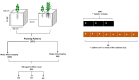
Methods: Hence, this study was designed to investigate the effect of maizesoybean intercropping on N uptake, N yield, N utilization use efficiency, and the associated nitrogen assimilatory enzymes of maize crops under different N fertilization for two consecutive years 2021-2022.
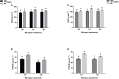
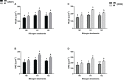
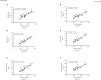
Results: The findings of the study showed that intercropping at the optimal N rate (N1) (250 kg N ha-1) increased significantly maize grain yield by 30 and 34%, residue yield by 30 and 37%, and 100-grain weight by 33 and 39% in the year 2021 and 2022, respectively. As compared with mono-cropping, at this optimal N rate, the respective increase (of maize's crop N yield indices) for 2021 and 2022 were 53 and 64% for grain N yield, and 53 and 68% for residue N yield. Moreover, intercropping at N1 resulted in higher grain N content by 28 and 31%, residue N content by 18 and 22%, and total N uptake by 65 and 75% in 2021 and 2022, respectively. The values for the land equivalent ratio for nitrogen yield (LERN) were greater than 1 in intercropping, indicating better utilization of N under the intercropping over mono-cropping. Similarly, intercropping increased the N assimilatory enzymes of maize crops such as nitrate reductase (NR) activity by 19 and 25%, nitrite reductase (NiR) activity by 20 and 23%, and glutamate synthase activity (GOGAT) by 23 and 27% in 2021 and 2022, respectively. Consequently, such increases resulted in improved nitrogen use efficiency indices such as N use efficiency (NUE), partial factor nitrogen use efficiency (PFNUE), nitrogen uptake efficiency (NUpE), and nitrogen agronomic efficiency (NAE) under intercropping than mono-cropping.
Conclusion: Thus, this suggests that maize-soybean intercropping under optimal N fertilization can improve the nitrogen status and nitrogen use efficiency of maize crops by regulating the nitrogen assimilatory enzymes, thereby enhancing its growth and yield. Therefore, prioritizing intercropping over an intensive mono-cropping system could be a better option for sustainable agricultural production.
Keywords: agricultural sustainability; maize-soybean intercropping; nitrogen assimilatory enzymes; nitrogen use efficiency; nitrogen yield.
Copyright © 2023 Nasar, Zhao, Khan, Gul, Gitari, Shao, Abbas, Haider, Iqbal, Ahmed, Rehman, Liang, Zhou and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Maize/soybean intercropping increases nutrient uptake, crop yield and modifies soil physio-chemical characteristics and enzymatic activities in the subtropical humid region based in Southwest China.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 May 21;24(1):434. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05061-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38773357 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of maize-alfalfa intercropping on the physiological characteristics, nitrogen uptake and yield of maize.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2020 Nov;22(6):1140-1149. doi: 10.1111/plb.13157. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2020. PMID: 32609937
-
Nitrogen fertilization coupled with iron foliar application improves the photosynthetic characteristics, photosynthetic nitrogen use efficiency, and the related enzymes of maize crops under different planting patterns.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 2;13:988055. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.988055. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36119633 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen assimilation in plants: current status and future prospects.J Genet Genomics. 2022 May;49(5):394-404. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2021.12.006. Epub 2021 Dec 30. J Genet Genomics. 2022. PMID: 34973427 Review.
-
The Role of Glutamine Synthetase (GS) and Glutamate Synthase (GOGAT) in the Improvement of Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Cereals.Biomolecules. 2023 Dec 10;13(12):1771. doi: 10.3390/biom13121771. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136642 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Organic material mulching regulated core microbial groups to promote soil carbon and nitrogen cycling and improve faba bean productivity under a triple-cropping system in purple soil hilly region of southwest China.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 16;16:1602633. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1602633. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40740326 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate on Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization in Waxy Sorghum Under Waxy Sorghum-Soybean Intercropping Systems.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 3;14(9):1384. doi: 10.3390/plants14091384. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40364413 Free PMC article.
-
Managing faba bean wilt disease through intercropping with wheat and reasonable nitrogen application: enhancing nutrient absorption and biochemical resistance in faba beans.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2024 Jun;30(6):1029-1046. doi: 10.1007/s12298-024-01466-1. Epub 2024 May 28. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2024. PMID: 38974356 Free PMC article.
-
Macrogenomics-Based Analysis of the Effects of Intercropped Soybean Photosynthetic Characteristics and Nitrogen-Assimilating Enzyme Activities on Yield at Different Nitrogen Levels.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 18;12(6):1220. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061220. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930602 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing production efficiency through optimizing plant density in maize-soybean strip intercropping.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Oct 11;15:1473786. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1473786. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39464277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anbessa Y., Juskiw P. (2012). Nitrogen fertilizer rate and cultivar interaction effects on nitrogen recovery, utilization efficiency, and agronomic performance of spring barley. ISRN Agron. 2012, 531647. doi: 10.5402/2012/531647 - DOI
-
- Ben M. R. (2016). Effect of nitrogen source and concentration on growth and activity of nitrogen assimilation enzymes in roots of a moroccan sorghum ecotype. Plant 4, 71–77. doi: 10.11648/j.plant.20160406.14 - DOI
-
- Dang K., Gong X., Zhao G., Wang H., Ivanistau A., Feng B. (2020). Intercropping alters the soil microbial diversity and community to facilitate nitrogen assimilation: A potential mechanism for increasing proso millet grain yield. Front. Microbiol. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.601054 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

