A genome wide association study to dissect the genetic architecture of agronomic traits in Andean lupin (Lupinus mutabilis)
- PMID: 36684793
- PMCID: PMC9846495
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1099293
A genome wide association study to dissect the genetic architecture of agronomic traits in Andean lupin (Lupinus mutabilis)
Abstract
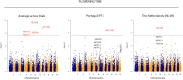
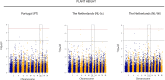
Establishing Lupinus mutabilis as a protein and oil crop requires improved varieties adapted to EU climates. The genetic regulation of strategic breeding traits, including plant architecture, growing cycle length and yield, is unknown. This study aimed to identify associations between 16 669 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and 9 agronomic traits on a panel of 223 L. mutabilis accessions, grown in four environments, by applying a genome wide association study (GWAS). Seven environment-specific QTLs linked to vegetative yield, plant height, pods number and flowering time, were identified as major effect QTLs, being able to capture 6 to 20% of the phenotypic variation observed in these traits. Furthermore, two QTLs across environments were identified for flowering time on chromosome 8. The genes FAF, GAMYB and LNK, regulating major pathways involved in flowering and growth habit, as well as GA30X1, BIM1, Dr1, HDA15, HAT3, interacting with these pathways in response to hormonal and environmental cues, were prosed as candidate genes. These results are pivotal to accelerate the development of L. mutabilis varieties adapted to European cropping conditions by using marker-assisted selection (MAS), as well as to provide a framework for further functional studies on plant development and phenology in this species.
Keywords: Lupinus mutabilis; SNP; association mapping; flowering time; molecular markers; plant architecture.
Copyright © 2023 Gulisano, Lippolis, van Loo, Paulo and Trindade.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diversity and Agronomic Performance of Lupinus mutabilis Germplasm in European and Andean Environments.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 10;13:903661. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.903661. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35755685 Free PMC article.
-
The genome of Lupinus mutabilis: Evolution and genetics of an emerging bio-based crop.Plant J. 2024 Nov;120(3):881-900. doi: 10.1111/tpj.17021. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 39264984
-
A GWAS study highlights significant associations between a series of indels in a FLOWERING LOCUS T gene promoter and flowering time in white lupin (Lupinus albus L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jul 29;24(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05438-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39075363 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study for Major Biofuel Traits in Sorghum Using Minicore Collection.Protein Pept Lett. 2021;28(8):909-928. doi: 10.2174/0929866528666210215141243. Protein Pept Lett. 2021. PMID: 33588716
-
Genetics and Breeding of Lupinus mutabilis: An Emerging Protein Crop.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Oct 30;10:1385. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01385. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31737013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ando E., Ohnishi M., Wang Y., Matsushita T., Watanabe A., Hayashi Y., et al. (2013). TWIN SISTER OF FT, GIGANTEA, and CONSTANS have a positive but indirect effect on blue light-induced stomatal opening in arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 162 (3), 1529–1538. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.217984 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Annicchiarico P., Nazzicari N., Notario T., Martin C. M., Romani M., Ferrari B., et al. (2021). Pea breeding for intercropping with cereals: variation for competitive ability and associated traits, and assessment of phenotypic and genomic selection strategies. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.731949 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avila C. M., Nadal S., Teresa Moreno M., Torres A. M. (2006). Development of a simple PCR-based marker for the determination of growth habit in vicia faba l. using a candidate gene approach. Mol. Breed. 17 (3), 185–190. doi: 10.1007/s11032-005-4075-4 - DOI
-
- Ávila C. M., Ruiz-Rodríguez M. D., Cruz-Izquierdo S., Atienza S. G., Cubero J. I., Torres A. M. (2017). Identification of plant architecture and yield-related QTL in vicia faba l. Mol. Breed. 37 (7), 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s11032-017-0688-7 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

