Air pollution burden of disease over highly populated states in the Middle East
- PMID: 36684989
- PMCID: PMC9853520
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1002707
Air pollution burden of disease over highly populated states in the Middle East
Abstract
Background: Recent epidemiological research has proven that air pollution triggers the risk of morbidity and mortality due to respiratory and cardiovascular-related diseases. More specifically, fine particulate matter with a diameter of <2.5 μm (PM2.5) can penetrate deeply into the lung and bloodstream, causing critical adverse effects on human health.
Objective: It is found that there is inadequate published research related to the health impact of ambient air pollution in the Middle East region. Some states are well studied, while others are not. This work aims to evaluate the health impact of long-term exposure to PM2.5 in the nine most populated countries in the Middle East region, with a total population of about 363 million (in 2012).
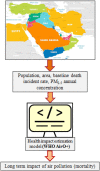
Methods: In this study, the human health impacts in terms of total mortality and the estimated attributable proportion (AP) due to long-term exposure to ambient PM2.5 were estimated using the World Health Organization method and software (AirQ+).
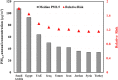
Results: In 2012, the annual median PM2.5 concentrations ranged from 34 μg/m3 in Turkey and Syria to 108 μg/m3 in Saudi Arabia. The total estimated mortalities in the nine most populated countries in the Middle East due to long-term exposure to fine particulate matter was about 152,925 (half of which were residents in Egypt). Moreover, the relative risk (RR) was the highest for Saudi Arabia at 1.8031 and the lowest for Turkey and Syria at a value of 1.1553. The highest AP (central value) was 44.5% in Saudi Arabia, while the lowest was 13.4% in Turkey and Syria.
Conclusions: The results indicate a significant impact of air pollution due to long-term exposure to fine particles resulting in early mortality. This urges the collaboration between the governments and different sectors to adopt stringent regulations to control the anthropogenic sources related to traffic and industrial emissions in the Middle East in order to reduce the health burden of air pollution.
Keywords: AirQ+; Middle East; WHO; air pollution; burden of disease; fine particulate matter; health impact; mortality.
Copyright © 2023 Isaifan.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Effatpanah M, Effatpanah H, Jalali S, Parseh I, Goudarzi G, Barzegar G, et al. Hospital admission of exposure to air pollution in Ahvaz megacity during 2010–2013. Clin Epidemiol Glob Heal. (2020) 8:550–6. 10.1016/j.cegh.2019.12.001 - DOI
-
- Hormati M, Mohammadi MJ, Iswanto AH, Mansourimoghadam S, Taifi A, Maleki H, et al. Consequences and health effects of toxic air pollutants emission by industries. J Air Pollut Heal. (2022) 7:95–108. 10.18502/japh.v7i1.8923 - DOI
-
- Geravandi S, Goudarzi GR, Vousoghi Niri M, Mohammadi MJ, Saeidimehr S. Estimate of cardiovascular and respiratory mortality related to sulfur dioxide pollutant in Ahvaz. J Environ Stud. (2015) 41:341–50.
-
- Amoatey P, Sicard P, De Marco A, Khaniabadi YO. Long-term exposure to ambient PM2, 5. and health impacts in megacity of Rome, Italy. Clin Epidemiol Glob Heal. (2019) 57:49–57. 10.1016/j.cegh.2019.11.009 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

