Research status and hotspots of medication safety in older adults: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 36684998
- PMCID: PMC9849762
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.967227
Research status and hotspots of medication safety in older adults: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Medication safety is a significant concern in healthcare. Research on medication safety for older adults has taken a broad approach, resulting in a range of proposals. At this juncture, it is necessary to identify the main contributors and establish the current developmental status of the principal research topics.
Objective: This study sets out to summarize the state-of-the-art in medication safety for older adults, identifying significant achievements, key topics, and emerging trends.
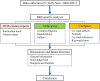
Methods: The Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC) database was searched for relevant documentation over the interval 1st January 2000 to 31st December 2021. Annual outputs and citations were identified from the WOS citation reports. CiteSpace and VOSviewer were adopted for bibliometric analysis and visualization that included the distribution of countries/regions, organizations, authors and journals, and an analysis of co-cited references and keywords.
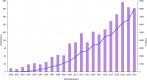
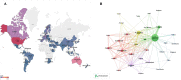
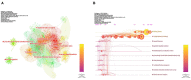
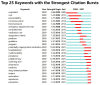
Results: A total of 1,638 documents were retrieved for bibliometric analysis, yielding 34.29 citations per document. Publications have increased over the past two decades, reaching 177 outputs in 2019. Our database encompasses 71 countries/regions, 2,347 organizations, and 7,040 authors. The United States ranks first in terms of scientific activity with 604 publications (36.87%). We have identified the University of Sydney as the most prolific organization (53 publications). J. T. Hanlon, J. H. Gurwitz, D. O'Mahony, and G. Onder are the most influential researchers in terms of publications and citations. The Journal of the American Geriatrics Society ranks first with 89 (5.43%) papers. In terms of major research directions, three topics have been identified from co-cited reference and keyword analysis: (1) estimation of the prevalence and variables associated with polypharmacy and potentially inappropriate medication; (2) analysis of interventions involving pharmacists and the associated impact; (3) patient experience and perception associated with medication use or pharmaceutical care.
Conclusion: Research on medication safety for older adults has progressed significantly over the past two decades. The United States, in particular, has made important contributions to this field. Polypharmacy and potentially inappropriate medication use, interventions involving pharmacists, patient experience and perception represent the current focus of research. Our findings suggest that these directions will continue as research hotspots in the future.
Keywords: aged; bibliometric analysis; hotspots; inappropriate prescribing; medication safety; patient safety; polypharmacy; research trends.
Copyright © 2023 Xie, Gu, Wang, Ni and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Global Highly Cited Publication Trends and Research Hotspots in Osteoporosis and Bone Metabolic Cells: A Bibliometric and Visualization Analysis from 2013 to 2023.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025;25(5):386-399. doi: 10.2174/0118715303300989240702043834. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 39005119
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Evolution and global research trends of immunity in diabetic nephropathy: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2004 to 2023.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Oct;56(10):3307-3321. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04081-x. Epub 2024 May 17. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38758346 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of global research trends on male osteoporosis: a neglected field deserves more attention.Arch Osteoporos. 2021 Oct 11;16(1):154. doi: 10.1007/s11657-021-01016-2. Arch Osteoporos. 2021. PMID: 34632530 Review.
-
Bibliometric and visualized analysis of ocular drug delivery from 2001 to 2020.J Control Release. 2022 May;345:625-645. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.03.031. Epub 2022 Mar 20. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35321827 Review.
Cited by
-
Research status and hotspots of oral frailty in older adults: a bibliometric analysis from 2013 to 2024.Front Oral Health. 2025 Jul 14;6:1533159. doi: 10.3389/froh.2025.1533159. eCollection 2025. Front Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40726966 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with perceived medication safety during transitions of care in patients with cancer: A secondary data analysis of a cross-sectional survey.Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2025 Jun;76:102857. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2025.102857. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40068277
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

