A novel technique of botulinum toxin injection around skull sutures for chronic migraine: A randomized controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 36685024
- PMCID: PMC9854915
- DOI: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_372_21
A novel technique of botulinum toxin injection around skull sutures for chronic migraine: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Migraine is a chronic headache manifested with attacks. Here we aimed to evaluate and compare the efficacy of 15-point Dysport injection with 31-point Xeomin injections.
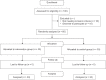
Materials and methods: This is a randomized clinical trial performed in 2020-2021 in Isfahan on patients with refractory chronic migraine. A total number of 60 patients entered the study. The pain of patients was also determined using headache impact test (HIT) questionnaire. Patients were randomized into two groups: Group 1 underwent 31-point Xeomin injection and Group 2 underwent 1 vial of Dysport injection into 15 points of the scalp.
Results: Our study revealed that the data regarding aura, nausea, vomit, photosensitivity, sensitivity to sounds and smells did not change significantly between two groups compared to the beginning of the study. Frequency, duration, intensity of headaches, and the mean HIT score of all patients improved significantly within 3 months after interventions. Comparing both groups showed no significant differences (P > 0.05). HIT score was decreased from 21.26 ± 3.58 before intervention to 15.51 ± 4.58 after 3 months in Group 1 and 22.23 ± 2.59-10.33 ± 2.26 in Group 2. In both groups, these changes were statistically significant (P < 0.001). Although we found more decrease of HIT score in Group 2 comparing with Group 1 (10.33 ± 2.26 vs. 15.51 ± 4.58), this difference was not statistically significant (P = 0.12).
Conclusion: Although Xeomin and Dysport injections are both effective and reduced pain in patients with chronic migraine, our new technique is probably better than the standard technique. Because the injection points are halved, increase patients comfort and reduce overall cost.
Keywords: Botulinum neurotoxin; Dysport; Xeomin; migraine.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Botulinum toxin type A as migraine preventive treatment in patients previously failing oral prophylactic treatment due to compliance issues.Headache. 2008 Jun;48(6):900-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.00953.x. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Headache. 2008. PMID: 18047501 Clinical Trial.
-
Botulinum toxin type a for the prophylaxis of chronic daily headache: subgroup analysis of patients not receiving other prophylactic medications: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study.Headache. 2005 Apr;45(4):315-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2005.05068.x. Headache. 2005. PMID: 15836567 Clinical Trial.
-
Monocentric Prospective Study into the Sustained Effect of Incobotulinumtoxin A (XEOMIN®) Botulinum Toxin in Chronic Refractory Migraine.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Jun 1;10(6):221. doi: 10.3390/toxins10060221. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29857565 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Botulinum toxin in migraine prophylaxis.J Neurol. 2004 Feb;251 Suppl 1:I8-11. doi: 10.1007/s00415-004-1103-y. J Neurol. 2004. PMID: 14991336 Review.
-
[Botulinum toxin treatment of hip adductor spasticity in multiple sclerosis].Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2001;113 Suppl 4:20-4. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2001. PMID: 15506048 Review. German.
References
-
- Burch RC, Buse DC, Lipton RB. Migraine: Epidemiology, burden, and comorbidity. Neurol Clin. 2019;37:631–49. - PubMed
-
- Martami F, Togha M, Seifishahpar M, Ghorbani Z, Ansari H, Karimi T, et al. The effects of a multispecies probiotic supplement on inflammatory markers and episodic and chronic migraine characteristics: A randomized double-blind controlled trial. Cephalalgia. 2019;39:841–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous