Role of acupuncture in critically ill patients: A systematic review
- PMID: 36685071
- PMCID: PMC9845654
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2022.10.005
Role of acupuncture in critically ill patients: A systematic review
Abstract
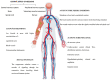
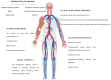
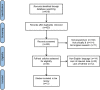
Acupuncture is part of a complex medical approach used in China for about 2000 years, known as Traditional Chinese Medicine, whose central assumption is that health occurs when the patterned energy flow throughout the body is balanced. Within this paradigm, acute illness occurs when a major state of imbalance or disruption arises, and the use of acupuncture may help in correcting these imbalances. While the Chinese hospital system often offers the integration of traditional and western medicine, in Europe and the United States this combined approach is infrequently practiced. However, several investigations have consistently shown the effectiveness of acupuncture for different aspects of critical illness. The aim of this systematic review is to increase the clinician's awareness of the current evidence regarding the use of acupuncture for the management of critically ill patients, both alone or as a complement to western medicine. The effects of acupuncture on critical illness, with a particular focus on respiratory function, pain and delirium treatment and prevention, circulatory function, nutritional support, and recovery after acute illness are explored and summarized, and evidence is provided that acupuncture is an acceptable and feasible option for the management of several aspects of critical illness. In addition, we suggest a practical selection of potentially useful acupuncture points in the critical care setting, with indications for simple localization and the correct puncture method.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Critical care; Systematic review; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2022 Center for Food and Biomolecules, National Taiwan University. Production and hosting by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
No author has to disclose any potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Further reading
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
