Dual actions of gallic acid and andrographolide trigger AdipoR1 to stimulate insulin secretion in a streptozotocin-induced diabetes rat model
- PMID: 36685073
- PMCID: PMC9845651
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2022.09.002
Dual actions of gallic acid and andrographolide trigger AdipoR1 to stimulate insulin secretion in a streptozotocin-induced diabetes rat model
Abstract
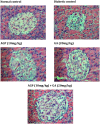
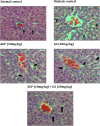
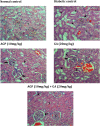
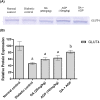
Common treatments for the management of diabetes have limitations due to side effects, hence the need for continuous research to discover new remedies with better therapeutic efficacy. Previously, we have reported that the combination treatment of gallic acid (20 mg/kg) and andrographolide (10 mg/kg) for 15 days demonstrated synergistic hypoglycemic activity in the streptozotocin (STZ)-induced insulin-deficient diabetes rat model. Here, we attempt to further elucidate the effect of this combination therapy at the biochemical, histological and molecular levels. Our biochemical analyses showed that the combination treatment significantly increased the serum insulin level and decreased the total cholesterol and triglyceride level of the diabetic animals. Histological examinations of H&E stained pancreas, liver, kidney and adipose tissues of combination-treated diabetic animals showed restoration to the normalcy of the tissues. Besides, the combination treatment significantly enhanced the level of glucose transporter-4 (GLUT4) protein expression in the skeletal muscle of treated diabetic animals compared to single compound treated and untreated diabetic animals. The molecular docking analysis on the interaction of gallic acid and/or andrographolide with the adiponectin receptor 1 (AdipoR1), a key component in the regulation of pancreatic insulin secretion, revealed a greater binding affinity of AdipoR1 to both compounds compared to individual compounds. Taken together, these findings suggest the combination of gallic acid and andrographolide as a potent therapy for the management of diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: AGP, Andrographolide; AdipoR1, Adiponectin receptor 1; Andrographolide; Diabetes mellitus; ELISA, Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; GA, Gallic acid; GLUT4, Glucose transporter-4; Gallic acid; H&E, Hematoxylin-eosin; Insulin; PBS, Phosphate buffer saline; STZ, Streptozotocin; TBST, Tris-buffered saline with 0.1% (v/v) Tween-20; adipoR1.
© 2022 Center for Food and Biomolecules, National Taiwan University. Production and hosting by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors want to declare that they have no conflict of interest associated with this publication.
Figures


References
-
- Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. World Health Organization; 2019.
-
- Whitlock R.H., Hougen I., Komenda P., Rigatto C., Clemens K.K., Tangri N. A safety comparison of metformin vs sulfonylurea initiation in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a retrospective cohort study. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(1):90–100. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.07.017. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
