Cinnamic aldehyde, an anti-inflammatory component in Du-Huo-Ji-Sheng-Tang, ameliorates arthritis in II collagenase and monosodium iodoacetate induced osteoarthritis rat models
- PMID: 36685080
- PMCID: PMC9845653
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2022.10.003
Cinnamic aldehyde, an anti-inflammatory component in Du-Huo-Ji-Sheng-Tang, ameliorates arthritis in II collagenase and monosodium iodoacetate induced osteoarthritis rat models
Abstract
Background and aim: Du-Huo-Ji-Sheng-Tang (DHJST) is a Chinese herbal formula used for arthralgia and arthritis treatment clinically. This study aims to evaluate the joint-protecting efficacy of DHJST and to identify the active constituents as the evaluation marker.
Experimental procedure: DHJST can be categorized into three recipes: Blood-tonifying-herbs Si-Wu-Tang (SWT), Wind-dampness-dispelling-herbs (WDH) and Qi-tonifying-herbs (TH). All formulas were used to explore the joint-protecting efficacies.
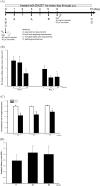
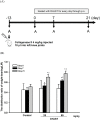
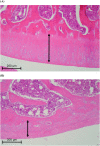
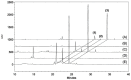
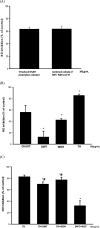
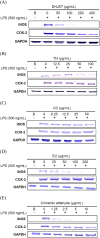
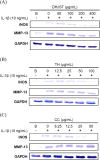
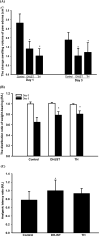
Results and conclusion: s: Firstly, DHJST could decrease the arthritis progression in the monosodium-iodoacetate-induced rat and cure arthritis in the type II collagenase-induced rat. Further, in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells, DHJST, TH and Cinnamomum cassia (CC), an ingredient in TH, were the most potent nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) inhibitors. The major components, cinnamic aldehyde, showed the strongest NO and PGE2 inhibition. Up-regulated inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 were inhibited by DHJST, TH, CC, and cinnamic aldehyde. In interleukin-1β-stimulated primary chondrocytes, upregulated iNOS was inhibited by DHJST, TH, Cinnamomum cassia, and cinnamic aldehyde. Upregulated matrix metalloprotease-13 was only inhibited by DHJST and TH and Eucommia ulmoides (EU) extract. Results suggest that DHJST presented joint-protective and cure arthritis effects. TH presented equal joint-protective effects as DHJST. The major anti-inflammatory ingredient in TH was Cinnamomum cassia in TH. And cinnamic aldehyde was the potent anti-inflammatory active compound in Cinnamomum cassia. Therefore, this study may facilitate the modern use of DHJST with TH as a simplified version but equally effective anti-osteoarthritic agents with cinnamic aldehyde as a quality control marker of DHJST and TH in osteoarthritis prevention or treatment.
Keywords: Arthritis; Cinnamic aldehyde; Cinnamomum cassia; Monosodium iodoacetate; Type II collagenase.
© 2022 Center for Food and Biomolecules, National Taiwan University. Production and hosting by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The author reports no conflicts of interest in this report.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
