Comparison of the accuracy of axial length measurement by different imaging methods in Sprague Dawley rats
- PMID: 36685229
- PMCID: PMC9854123
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1106904
Comparison of the accuracy of axial length measurement by different imaging methods in Sprague Dawley rats
Abstract
Background: Obtaining accurate axial length (AL) is very important for the establishment of animal models of myopia. The purpose of this study is to compare the accuracy of Quantel A-B scan, OD-1 A scan, and vernier caliper in measuring AL in Sprague Dawley (SD) rats.
Methods: In total, 60 5-week-old SD rats were divided into female rat group (n = 30) and male rat group (n = 30). Quantel A-B scan and OD-1 A scan were, respectively, used to measure the AL of both eyes of each living rat, and vernier caliper was used to measure the anterior-posterior diameter of each rat's eyeball. Besides, the correlation between refractive error (RE) and AL measured by different instruments was evaluated, and the accuracy of the three measurement methods was compared according to gender and left/right eyes.
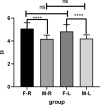
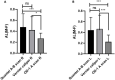
Results: There were significant differences in AL and diopter of SD rats at the same age (p < 0.05). the AL of male rats was greater than that of female rats, while diopter (D) was the opposite; There was no significant difference in AL and D between left and right eyes in the same SD rats (p > 0.05); There were statistical differences among the three measurement methods (p < 0.05), AL measured by vernier caliper was the largest, followed by Quantel A-B scan, OD-1 A scan; Difference in AL between male and female was not statistically significant between the results obtained by Quantel A-B scan and vernier caliper (p > 0.05), but there were statistically significant differences between the other two measurement methods (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Sex is the influencing factor of AL and RE. Imaging measurement can accurately measure the AL in living small rodents. Compared with OD-1 A scan, Quantel A-B scan may be more accurate.
Keywords: OD-1 A scan; Quantel A-B scan; axial length; measuring method; vernier caliper.
Copyright © 2023 Wu, Luo, Feng, Yang, Fan, Cen and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
XC was employed by WestChina-Frontier PharmaTech Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Accuracy of axial length measurements from immersion B-scan ultrasonography in highly myopic eyes.Int J Ophthalmol. 2014 Jun 18;7(3):441-5. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2014.03.10. eCollection 2014. Int J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24967188 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of segmented measurement of axial length in ultra-high myopia filled with silicone oil using immersion B-scan ultrasonography.Int J Ophthalmol. 2022 May 18;15(5):793-799. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2022.05.16. eCollection 2022. Int J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35601170 Free PMC article.
-
[Accuracy of immersion B-scan ultrasound biometry in high myopic patients with cataract].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Jan;50(1):32-6. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24709131 Chinese.
-
Superior Measurement Accuracy of Digital Thickness Gauge Versus Digital Vernier Caliper in Determining Venous Tissue Thickness.Cureus. 2024 Sep 2;16(9):e68442. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68442. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39360102 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the accuracy of Canon KU-1 IOL measurer and VPLUS A/B scanner in axial length measurement.Yan Ke Xue Bao. 2003 Sep;19(3):150-2, 183. Yan Ke Xue Bao. 2003. PMID: 14574969
Cited by
-
Integrating a Fundus Camera with High-Frequency Ultrasound for Precise Ocular Lesion Assessment.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Feb 29;14(3):127. doi: 10.3390/bios14030127. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534234 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

