Cathepsin-B inhibitor CA-074 attenuates retinopathy and optic neuritis in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis induced in SJL/J mice
- PMID: 36685301
- PMCID: PMC9845124
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2022.11.013
Cathepsin-B inhibitor CA-074 attenuates retinopathy and optic neuritis in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis induced in SJL/J mice
Abstract
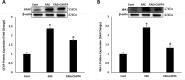
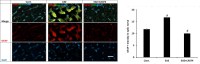
The complicated multiple sclerosis (MS) can exhibit subacute sight deterioration and can lead to total deprivation of vision. In the current work, we explored the therapeutic outcome of Cathepsin B inhibitor (CA-074) against retinopathy and optic neuritis (ON) caused by experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) induced by proteolipid protein peptide (PLP) in female SJL/J mice. A daily dose of 10 mg/kg CA-074 was administered to the EAE mice intraperitoneally for 14 days from day 14 post-immunization until day 28. The Western blot and immunofluorescence analyses show inflammation in the optic nerve through the elevation of iNOS and NFkB markers in EAE mice. Optic neuritis was reported which is a consequence of demyelination and axon injury, estimated with the reduction in myelin basic protein (MBP). The glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expression level was found to be elevated in the retina of EAE mice which confirmed the retinopathy. The administration of CA-074 ameliorated optic neuritis and retinopathy by reducing inflammation. The treatment with CA-074 also reduced the demyelination and axonal injuries in the EAE mice. The findings of this study have shown the protective effect of CA-074 in the case of retinopathy and ON inflicted by EAE in SJL/J mice.
Keywords: Demyelination; Multiple sclerosis; Neurodegeneration; Optic Neuritis; Retinopathy.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Monitoring retinal changes with optical coherence tomography predicts neuronal loss in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Nov 4;16(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1583-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31684959 Free PMC article.
-
Laquinimod protects the optic nerve and retina in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Jun 14;15(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1208-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29903027 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Nrf2 exacerbates the visual deficits and optic neuritis elicited by experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Mol Vis. 2016 Dec 30;22:1503-1513. eCollection 2016. Mol Vis. 2016. PMID: 28050123 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect and mechanism of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide against optic neuritis in mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Sep;98:107846. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107846. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34174704
-
Pterostilbene Protects the Optic Nerves and Retina in a Murine Model of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis via Activation of SIRT1 Signaling.Neuroscience. 2022 Apr 1;487:35-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.01.016. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Neuroscience. 2022. PMID: 35090883
Cited by
-
Cathepsin B inhibition blocks amyloidogenesis in the mouse models of neurological lysosomal diseases MPS IIIC and sialidosis.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2025 Feb 11;33(1):101432. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2025.101432. eCollection 2025 Mar 13. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2025. PMID: 40092638 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting SMOX Preserves Optic Nerve Myelin, Axonal Integrity, and Visual Function in Multiple Sclerosis.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 21;15(2):158. doi: 10.3390/biom15020158. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40001462 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Profiling and Therapeutic Targeting of Oxidative Stress in Autoimmune Encephalitis.J Mol Neurosci. 2025 Mar 19;75(2):38. doi: 10.1007/s12031-025-02332-9. J Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40106157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansari M.A., Nadeem A., Alshammari M.A., Attia S.M., Bakheet S.A., Khan M.R., Albekairi T.H., Alasmari A.F., Alhosaini K., Alqahtani F., Al-Mazroua H.A., Ahmad S.F. Cathepsin B inhibitor alleviates Th1, Th17, and Th22 transcription factor signaling dysregulation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Exp. Neurol. 2022;351:113997. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2022.113997. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

