Accelerated biodecolorization and detoxification of synthetic textile dye Acid Maroon V by bacterial consortium under redox mediator system
- PMID: 36685318
- PMCID: PMC9845506
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03466-6
Accelerated biodecolorization and detoxification of synthetic textile dye Acid Maroon V by bacterial consortium under redox mediator system
Abstract
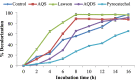
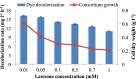
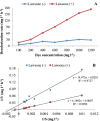
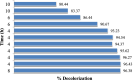
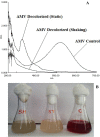
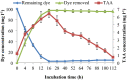
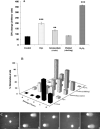
The treatment of textile industrial wastewater is an important concern owing to its negative impact on the biosphere. The present study highlighted dye decolorization potential of bacterial consortium EDPA containing Enterobacter dissolvens AGYP1 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa AGYP2 in the presence of redox mediators. Rapid decolorization of Acid Maroon V (100 mg l-1) was achieved in the presence of lawsone compared to other redox mediators. The dye decolorization was best fitted with first order kinetics with higher reaction kinetics (k1 = 0.328 h-1) and regression coefficient (R2 = 0.979). The removal of dye by the consortium was 1.47 times faster in 8 h with 0.01 mM lawsone. The consortium EDPA was able to decolorize 1200 mg l-1 concentration of dye with apparent R max , K m and R max /K m values 1000 mg l-1 h-1, 5000 mg l-1 and 0.2 h-1, respectively. The lawsone-mediated system could decolorize the dye 80.44% in 10 h at the end of 11 dye spiking cycle. The superior biodecolorization of 14 different textile dyes was obtained in the presence of lawsone-mediated system. The intracellular enzyme activities of azoreductase, NADH-DCIP reductase, laccase, manganese peroxidase and lignin peroxidase increased significantly. The sequential microaerophilic-aerobic incubation resulted into 89.31% reduction of total aromatic amines. The microbial toxicity, phytotoxicity and genotoxicity measurements revealed biotransformation of toxic nature of dye Acid Maroon V into non-toxic metabolites by the action of consortium EDPA, and thus its suitability for biotreatment of dye containing industrial effluents.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13205-023-03466-6.
Keywords: Acid Maroon V; Consortium EDPA; Decolorization; Lawsone; Toxicity.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biological treatment of textile dyes by agar-agar immobilized consortium in a packed bed reactor.Water Environ Res. 2015 Mar;87(3):242-51. doi: 10.2175/106143015x14212658613190. Water Environ Res. 2015. PMID: 25842535
-
Development of a bioreactor for remediation of textile effluent and dye mixture: a plant-bacterial synergistic strategy.Water Res. 2013 Mar 1;47(3):1035-48. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.11.007. Epub 2012 Nov 23. Water Res. 2013. PMID: 23245543
-
Biodegradation and detoxification of textile azo dyes by bacterial consortium under sequential microaerophilic/aerobic processes.EXCLI J. 2015 Jan 29;14:158-74. doi: 10.17179/excli2014-642. eCollection 2015. EXCLI J. 2015. PMID: 26417357 Free PMC article.
-
Decolorization of Metanil Yellow G by a halophilic alkalithermophilic bacterial consortium.Bioresour Technol. 2020 Nov;316:123923. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123923. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Bioresour Technol. 2020. PMID: 32763804
-
Textile Dye Biodecolorization by Manganese Peroxidase: A Review.Molecules. 2021 Jul 21;26(15):4403. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154403. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361556 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambika KV, Jamwal A, Kumar V, Singh D. Green bioprocess for degradation of synthetic dyes mixture using consortium of laccase-producing bacteria from Himalayan niches. J Environ Manage. 2022;310:114764. - PubMed
-
- Bafana A, Devi SS, Krishnamurthi K, Chakrabarti T. Kinetics of decolourisation and biotransformation of direct black 38 by C. hominis and P. stutzeri. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007;74(5):1145–1152. - PubMed
-
- Banat IM, Nigam P, Singh D, Marchant R. Microbial decolorization of textile-dyecontaining effluents: a review. Bioresour Technol. 1996;58(3):217–227.
-
- Barathi S, Aruljothi KN, Karthik C, Padikasan IA, Ashokkumar V. Biofilm mediated decolorization and degradation of reactive red 170 dye by the bacterial consortium isolated from the dyeing industry wastewater sediments. Chemosphere. 2022;286:131914. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

