Draft genome sequence of Joostella atrarenae M1-2T with cellulolytic and hemicellulolytic ability
- PMID: 36685320
- PMCID: PMC9845502
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03472-8
Draft genome sequence of Joostella atrarenae M1-2T with cellulolytic and hemicellulolytic ability
Abstract
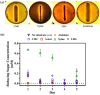
The halophilic genus Joostella is one of the least-studied genera in the family of Flavobacteriaceae. So far, only two species were taxonomically identified with limited genomic analysis in the aspect of application has been reported. Joostella atrarenae M1-2T was previously isolated from a seashore sample and it is the second discovered species of the genus Joostella. In this project, the genome of J. atrarenae M1-2T was sequenced using NovaSeq 6000. The final assembled genome is comprised of 71 contigs, a total of 3,983,942 bp, a GC ratio of 33.2%, and encoded for 3,416 genes. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of J. atrarenae M1-2T shows 97.3% similarity against J. marina DSM 19592T. Genome-genome comparison between the two strains by ANI, dDDH, AAI, and POCP shows values of 80.8%, 23.3%, 83.4%, and 74.1% respectively. Pan-genome analysis shows that strain M1-2T and J. marina DSM 19592T shared a total of 248 core genes. Taken together, strain M-2T and J. marina DSM 19592T belong to the same genus but are two different species. CAZymes analysis revealed that strain M1-2T harbors 109 GHs, 40 GTs, 5 PLs, 9 CEs, and 6 AAs. Among these CAZymes, while 5 genes are related to cellulose degradation, 12 and 24 genes are found to encode for xylanolytic enzymes and other hemicellulases that involve majorly in the side chain removal of the lignocellulose structure, respectively. Furthermore, both the intracellular and extracellular crude extracts of strain M1-2T exhibited enzymatic activities against CMC, xylan, pNPG, and pNPX substrates, which corresponding to endoglucanase, xylanase, β-glucosidase, and β-xylosidase, respectively. Collectively, description of genome coupled with the enzyme assay results demonstrated that J. atrarenae M1-2T has a role in lignocellulosic biomass degradation, and the strain could be useful for lignocellulosic biorefining.
Keywords: Cellulase; Flavobacteriaceae; Halophile; Hemicellulase; Joostella.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestOn behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A description of Joostella sp. strain CR20 with potential biotechnological applications.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2024 Nov 29;118(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s10482-024-02045-w. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2024. PMID: 39613983
-
Joostella atrarenae sp. nov., a novel member of the Flavobacteriaceae originating from the black sea sand of Jeju Island.Curr Microbiol. 2011 Feb;62(2):606-11. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9750-y. Epub 2010 Sep 5. Curr Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 20820783
-
Draft genome sequence of Hahella sp. CR1 and its ability in producing cellulases for saccharifying agricultural biomass.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Jul 7;205(8):278. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03617-6. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37420023
-
Complete genome sequence of Rhodothermaceae bacterium RA with cellulolytic and xylanolytic activities.3 Biotech. 2018 Aug;8(8):376. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1391-z. Epub 2018 Aug 13. 3 Biotech. 2018. PMID: 30105201 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulose- and xylan-degrading yeasts: Enzymes, applications and biotechnological potential.Biotechnol Adv. 2022 Oct;59:107981. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.107981. Epub 2022 May 14. Biotechnol Adv. 2022. PMID: 35580749 Review.
References
-
- Cardoso J, Fonseca L, Abrantes I. α-l-fucosidases from Bursaphelenchus xylophilus secretome—Molecular characterization and their possible role in breaking down plant cell walls. Forests. 2020;11:265. doi: 10.3390/f11030265. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

