A novel solvent-free co-grinding preparation improves curcumin bioavailability in healthy volunteers: A single-center crossover study
- PMID: 36685407
- PMCID: PMC9852671
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e12829
A novel solvent-free co-grinding preparation improves curcumin bioavailability in healthy volunteers: A single-center crossover study
Abstract
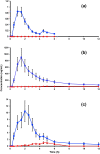
Curcumin, from the rhizome of turmeric (Curcuma longa L.), has a wide variety of biological activities. Unfortunately, its poor water-solubility greatly limits its bioavailability. The purpose of this study was to evaluate CUMINUP60®, a novel preparation utilizing a solvent-free, co-grinding method designed to improve curcumin's bioavailability. We performed a single-center crossover experiment to compare the new product with standard 95% curcumin in the blood plasma of twelve healthy adults (10 males, 2 females). Total bioavailability of curcumin and its sulfate and glucuronide conjugates from the test product, measured by their areas under the curve over 12 h (AUC0-T), showed a combined increase of 178-fold over standard curcumin and its conjugates from the reference product. The new product represents a significant improvement for providing greater bioavailability of curcumin, as compared with several other branded preparations. It therefore has broad applications for preparing curcumin as a more effective health ingredient in functional foods, beverages, and nutraceuticals.
Keywords: CUMINUP60®; Curcumin; Oral bioavailability; Pharmacokinetics.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as a potential competing interest: CUMINUP60® is the registered trademark name of Chenland Nutritionals, Inc., for the test product used in the present study. Chenland Nutritionals, Inc., had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Jurenka J.S. Anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin, a major constituent of Curcuma longa: a review of preclinical and clinical research. Alternative Med. Rev. 2009;14(2):141–153. PMID: 19594223. - PubMed
-
- Kishimoto A., Imaizumi A., Wada H., Yamakage H., Satoh-Asahara N., Hashimoto T., Hasegawa K. Newly developed highly bioavailable curcumin formulation, curcuRougeTM, reduces neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in the elderly: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2021;67(4):249–252. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.67.249. PMID: 34471000. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources