Case report: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in a severe case of Aicardi-Goutières syndrome with an IFIH1 gain-of-function mutation mimicking combined immunodeficiency
- PMID: 36685504
- PMCID: PMC9846174
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1033513
Case report: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in a severe case of Aicardi-Goutières syndrome with an IFIH1 gain-of-function mutation mimicking combined immunodeficiency
Abstract
Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (AGS) is a genetically determined early-onset progressive encephalopathy caused by mutations leading to overexpression of type I interferon (IFN) and resulting in various clinical phenotypes. A gain-of-function (GOF) mutation in the IFIH1 gene is associated with robust production of type I IFN and activation of the Janus kinase (JAK) signal transducer and activator of the transcription (STAT) pathway, which can cause AGS type 7. We detail the clinical case of an infant who initially presented with Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP), had recurrent respiratory infections, and was later treated with a JAK inhibitor, baricitinib, because of a genetically confirmed GOF mutation in the IFIH1 gene. This spectrum of IFIH1 GOF mutations with overlapping features of hyperinflammation and severe opportunistic infection, which mimics combined immunodeficiency (CID), has not been described before. In this case, therapy with baricitinib effectively blocked IFN-α activation and reduced STAT1 signaling but had no effect on the progression of the neurological disease.
Keywords: Aicardi–Goutières syndrome (AGS); IFIH1 gene; Janus kinase inhibitor; combined immune deficiency; interferonopathy.
Copyright © 2023 Železnik, Soltirovska Šalamon, Debeljak, Goropevšek, Šuštar, Ključevšek, Ihan and Avčin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
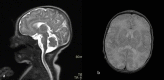
Figures


References
-
- Crow YJ, Chase DS, Lowenstein Schmidt J, Szynkiewicz M, Forte G, Gornall HL, et al. Characterization of human disease phenotypes associated with mutations in TREX1 , RNASEH2A, RNASEH2B, RNASEH2C, SAMHD1. ADAR, and IFIH1. Am J Med Genet Part A (2015) 167A(2):296–312. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36887 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

