Comparing the pertussis antibody levels of healthy children immunized with four doses of DTap-IPV/Hib (Pentaxim) combination vaccine and DTaP vaccine in Quzhou, China
- PMID: 36685526
- PMCID: PMC9852981
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1055677
Comparing the pertussis antibody levels of healthy children immunized with four doses of DTap-IPV/Hib (Pentaxim) combination vaccine and DTaP vaccine in Quzhou, China
Abstract
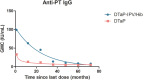
Despite the high coverage of pertussis vaccines in high-income countries, pertussis resurgence has been reported in recent years, and has stimulated interest in the effects of vaccines and vaccination strategies. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against pertussis toxoid (PT), filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA), and pertactin (PRN) after immunization with four doses of co-purified or component vaccines were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Serological data of PT-IgG geometric mean concentrations (GMCs) over time since vaccination were used to fit the mathematical models. A total of 953 children were included in this study; 590 participants received four doses of the component acellular vaccine and 363 participants received four doses of the co-purified acellular vaccine. The GMCs and the seropositivity rate of pertussis IgG were significantly influenced by the production methods, and the immunogenicity of the component acellular vaccine was superior to that of the co-purified acellular vaccine. The fitted mathematical models for the component acellular vaccine and the co-purified acellular vaccine were Y=91.20e-0.039x and Y=37.71x-0.493, respectively. The initial GMCs of the component acellular vaccine was higher than that of the co-purified acellular vaccine, but both were similar at 72 months after immunization. Pertussis IgG levels waned over time after four doses of acellular pertussis vaccine, regardless of whether component or co-purified vaccine was used. The development and promotion of component acellular pertussis vaccines should be accelerated in China, and booster doses of pertussis vaccine in adolescents, adults, and pregnant women should be employed.
Keywords: Acellular pertussis vaccine; healthy children; mathematic model; pertussis IgG; purification methods.
Copyright © 2023 Yin, Zheng, Fang, Wen, Wang, Li, Gong and Xiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of maternal diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis vaccination on pertussis booster immune responses in toddlers: Follow-up of a randomized trial.Vaccine. 2021 Mar 12;39(11):1598-1608. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.02.001. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Vaccine. 2021. PMID: 33612341 Clinical Trial.
-
Sustained efficacy during the first 6 years of life of 3-component acellular pertussis vaccines administered in infancy: the Italian experience.Pediatrics. 2001 Nov;108(5):E81. doi: 10.1542/peds.108.5.e81. Pediatrics. 2001. PMID: 11694665 Clinical Trial.
-
An evaluation of the safety and immunogenicity of a five-component acellular pertussis, diphtheria, and tetanus toxoid vaccine (DTaP) when combined with a Haemophilus influenzae type b-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine (PRP-T) in Taiwanese infants.Pediatrics. 1999 Jan;103(1):25-30. doi: 10.1542/peds.103.1.25. Pediatrics. 1999. PMID: 9917435 Clinical Trial.
-
New acellular pertussis-containing paediatric combined vaccines.Vaccine. 1999 Mar 26;17(13-14):1650-6. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(98)00422-8. Vaccine. 1999. PMID: 10194818 Review.
-
Reduced-antigen, combined diphtheria, tetanus and acellular pertussis vaccine, adsorbed (Boostrix®): a review of its properties and use as a single-dose booster immunization.Drugs. 2012 Sep 10;72(13):1765-91. doi: 10.2165/11209630-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22931522 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiological characteristics and survival analysis of pertussis in Quzhou.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2420448. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2420448. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39474925 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Effectiveness of 3 Types of Acellular Pertussis Vaccines Among Children Aged 3 Months-16 Years in Lu'an, China: A Matched Case-Control Study.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 10;12(2):ofaf082. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf082. eCollection 2025 Feb. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39968308 Free PMC article.
-
Surveillance for adverse events following immunization with DTaP-containing combination vaccines in Linping, China, 2019-2022.Front Public Health. 2024 Mar 26;12:1278513. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1278513. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38596516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Pertussis (Whooping cough). Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/index.html.
-
- Tessier E, Campbell H, Ribeiro S, Andrews N, Stowe J, Nicholls M, et al. . Investigation of a pertussis outbreak and comparison of two acellular booster pertussis vaccines in a junior school in south East England, 2019. Euro Surveillance (2021) 26(12):2000244. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.12.2000244 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical