α1-adrenoceptor stimulation ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury by inhibiting alveolar macrophage inflammatory responses through NF-κB and ERK1/2 pathway in ARDS
- PMID: 36685596
- PMCID: PMC9853445
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1090773
α1-adrenoceptor stimulation ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury by inhibiting alveolar macrophage inflammatory responses through NF-κB and ERK1/2 pathway in ARDS
Abstract
Introduction: Catecholamines such as norepinephrine or epinephrine have been reported to participate in the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) by activating adrenergic receptors (ARs). But the role of α1-AR in this process has yet to be elucidated.
Methods: In this study, ARDS mouse model was induced by intratracheal instillation of lipopolysaccharide. After treatment with α1-AR agonist phenylephrine or antagonist prazosin, lung pathological injury, alveolar barrier disruption and inflammation, and haemodynamic changes were evaluated. Cytokine levels and cell viability of alveolar macrophages were measured in vitro. Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), mitogen-activated protein kinase, and Akt signalling pathways were analysed by western blot.
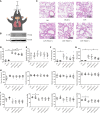
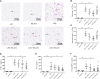
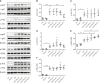
Results: It showed that α1-AR activation alleviated lung injuries, including reduced histopathological damage, cytokine expression, and inflammatory cell infiltration, and improved alveolar capillary barrier integrity of ARDS mice without influencing cardiovascular haemodynamics. In vitro experiments suggested that α1-AR stimulation inhibited secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, CXCL2/MIP-2, and promoted IL-10 secretion, but did not affect cell viability. Moreover, α1-AR stimulation inhibited NF-κB and enhanced ERK1/2 activation without significantly influencing p38, JNK, or Akt activation.
Discussion: Our studies reveal that α1-AR stimulation could ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury by inhibiting NF-κB and promoting ERK1/2 to suppress excessive inflammatory responses of alveolar macrophages.
Keywords: NF-κb; acute respiratory distress syndrome; alveolar macrophage; inflammation; α1 adrenergic receptor.
Copyright © 2023 Cong, Yang, Zeng, Wu, Zhao, Shen, Xiao and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
α2A-adrenoceptor deficiency attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury by increasing norepinephrine levels and inhibiting alveolar macrophage activation in acute respiratory distress syndrome.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Jul 31;134(14):1957-1971. doi: 10.1042/CS20200586. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32643759
-
α2A -AR antagonism by BRL-44408 maleate attenuates acute lung injury in rats with downregulation of ERK1/2, p38MAPK, and p65 pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Oct;235(10):6905-6914. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29586. Epub 2020 Jan 31. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32003020
-
α₁ adrenoceptor activation by norepinephrine inhibits LPS-induced cardiomyocyte TNF-α production via modulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Feb;18(2):263-73. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12184. Epub 2013 Dec 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24304472 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking NF-κB: an inflammatory issue.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2011 Nov;8(6):497-503. doi: 10.1513/pats.201101-009MW. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2011. PMID: 22052926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using the sympathetic system, beta blockers and alpha-2 agonists, to address acute respiratory distress syndrome.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Sep 30;139:112670. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112670. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39018694 Review.
Cited by
-
Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells by IFN-γ and IL-1β Ameliorate Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome through Enhancing Homing Effect and Immunomodulation.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2025 Mar 1;33(2):311-324. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2025.004. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2025. PMID: 39973472 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation of TTC4 interaction with HSP70 inhibits pyroptosis in macrophages of sepsis-induced lung injury by NLRP3 inflammation.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Nov 15;13(11):5122-5137. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38058818 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of apigetrin in pseudo-SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammatory and pulmonary fibrosis in vitro model.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 24;14(1):14545. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65447-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38914619 Free PMC article.
-
Zang Siwei Qingfei Mixture Alleviates Inflammatory Response to Attenuate Acute Lung Injury by the ACE2/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Mice.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(19):2871-2884. doi: 10.2174/0113862073259884231024111447. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37957855
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

