Alkaloid production and response to natural adverse conditions in Peganum harmala: in silico transcriptome analyses
- PMID: 36685700
- PMCID: PMC9837557
- DOI: 10.5114/bta.2022.120706
Alkaloid production and response to natural adverse conditions in Peganum harmala: in silico transcriptome analyses
Abstract
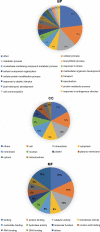
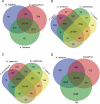
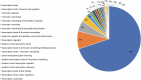
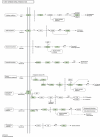
Peganum harmala is a valuable wild plant that grows and survives under adverse conditions and produces pharmaceutical alkaloid metabolites. Using different assemblers to develop a transcriptome improves the quality of assembled transcriptome. In this study, a concrete and accurate method for detecting stress-responsive transcripts by comparing stress-related gene ontology (GO) terms and public domains was designed. An integrated transcriptome for P. harmala including 42 656 coding sequences was created by merging de novo assembled transcriptomes. Around 35 000 transcripts were annotated with more than 90% resemblance to three closely related species of Citrus, which confirmed the robustness of the assembled transcriptome; 4853 stress-responsive transcripts were identified. CYP82 involved in alkaloid biosynthesis showed a higher number of transcripts in P. harmala than in other plants, indicating its diverse alkaloid biosynthesis attributes. Transcription factors (TFs) and regulatory elements with 3887 transcripts comprised 9% of the transcriptome. Among the TFs of the integrated transcriptome, cystein2/histidine2 (C2H2) and WD40 repeat families were the most abundant. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) signaling map and the plant hormone signal transduction map showed the highest assigned genes to these pathways, suggesting their potential stress resistance. The P. harmala whole-transcriptome survey provides important resources and paves the way for functional and comparative genomic studies on this plant to discover stress-tolerance-related markers and response mechanisms in stress physiology, phytochemistry, ecology, biodiversity, and evolution. P. harmala can be a potential model for studying adverse environmental cues and metabolite biosynthesis and a major source for the production of various alkaloids.
Keywords: RNA-Seq; SSR; halophyte; model plant; transcription factor.
© 2022 Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Analysis of the Dendrobium officinale transcriptome reveals putative alkaloid biosynthetic genes and genetic markers.Gene. 2013 Sep 15;527(1):131-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.05.073. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23756193
-
Exploring drought stress-regulated genes in senna (Cassia angustifolia Vahl.): a transcriptomic approach.Funct Integr Genomics. 2017 Jan;17(1):1-25. doi: 10.1007/s10142-016-0523-y. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Funct Integr Genomics. 2017. PMID: 27709374
-
Transcriptome analysis and differential gene expression profiling of two contrasting quinoa genotypes in response to salt stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Dec 30;20(1):568. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02753-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 33380327 Free PMC article.
-
Subchronic toxicity and concomitant toxicokinetics of long-term oral administration of total alkaloid extracts from seeds of Peganum harmala Linn: A 28-day study in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Jun 28;238:111866. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.111866. Epub 2019 Apr 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30970283
-
Alkaloids of Peganum harmala: Anticancer Biomarkers with Promising Outcomes.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(2):185-196. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666201125103941. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 33238864 Review.
References
-
- Ababou A., Chouieb M., Bouthiba A., Saidi D., M’Hamedi Bouzina M., Mederbal K. (2013) Spatial pattern analysis of Peganum harmala on the salted lower Chelif plain, Algeri. Turkish J. Bot. 37: 111–121.
-
- Abbott L.B., Bettmann G.T., Sterling T.M. (2008) Physiology and recovery of African rue (Peganum harmala) seedlings under water-deficit stress. Weed Sci. 56: 52–57.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
