One-year stable pilot-scale operation demonstrates high flexibility of mainstream anammox application
- PMID: 36685722
- PMCID: PMC9845764
- DOI: 10.1016/j.wroa.2023.100166
One-year stable pilot-scale operation demonstrates high flexibility of mainstream anammox application
Abstract
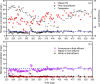
Mainstream nitrogen removal via anammox is widely recognized as a promising wastewater treatment process. However, its application is challenging at large scale due to unstable suppression of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB). In this study, a pilot-scale mainstream anammox process was implemented in an Integrated Fixed-film Activated Sludge (IFAS) configuration. Stable operation with robust NOB suppression was maintained for over one year. This was achieved through integration of three key control strategies: i) low dissolved oxygen (DO = 0.4 ± 0.2 mg O2/L), ii) regular free nitrous acid (FNA)-based sludge treatment, and iii) residual ammonium concentration control (NH4 + with a setpoint of ∼8 mg N/L). Activity tests and FISH demonstrated that NOB barely survived in sludge flocs and were inhibited in biofilms. Despite receiving organic-deficient wastewater from a pilot-scale High-Rate Activated Sludge (HRAS) system as the feed, the system maintained a stable effluent total nitrogen concentration mostly below 10 mg N/L, which was attributed to the successful retention of anammox bacteria. This study successfully demonstrated large-scale long-term mainstream anammox application and generated new practical knowledge for NOB control and anammox retention.
Keywords: Autotrophic nitrogen removal from wastewater; Bioenergy recovery; Effluent quality; Mainstream anammox; NOB suppression.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Agrawal S., Seuntjens D., Cocker P.D., Lackner S., Vlaeminck S.E. Success of mainstream partial nitritation/anammox demands integration of engineering, microbiome and modeling insights. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018;50:214–221. - PubMed
-
- APHA . 2005. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater.
-
- Blackburne R., Yuan Z., Keller J. Partial nitrification to nitrite using low dissolved oxygen concentration as the main selection factor. Biodegradation. 2008;19(2):303–312. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y., van Loosdrecht M.C., Daigger G.T. Mainstream partial nitritation-anammox in municipal wastewater treatment: status, bottlenecks, and further studies. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017;101(4):1365–1383. - PubMed
-
- Chen G., Li J., Wei J., Zeng J., Zhang Y., Bian W., Deng H. Nitritation via heat shock using immobilized active sludge aggregates. Desalinat. Water Treat. 2016;57(48–49):22779–22787.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

