Biomechanical investigation of maxillary implant-supported full-arch prostheses produced with different framework materials: a finite elements study
- PMID: 36685790
- PMCID: PMC9832146
- DOI: 10.4047/jap.2022.14.6.346
Biomechanical investigation of maxillary implant-supported full-arch prostheses produced with different framework materials: a finite elements study
Abstract
Purpose: Four and six implant-supported fixed full-arch prostheses with various framework materials were assessed under different loading conditions.
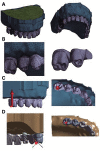
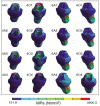
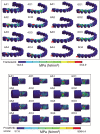
Materials and methods: In the edentulous maxilla, the implants were positioned in a configuration of four to six implant modalities. CoCr, Ti, ZrO2, and PEEK materials were used to produce the prosthetic structure. Using finite element stress analysis, the first molar was subjected to a 200 N axial and 45° oblique force. Stresses were measured on the bone, implants, abutment screw, abutment, and prosthetic screw. The Von Mises, maximum, and minimum principal stress values were calculated and compared.
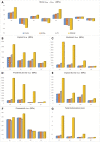
Results: The maximum and minimum principal stresses in bone were determined as CoCr < ZrO2 < Ti < PEEK. The Von Mises stresses on the implant, implant screw, abutment, and prosthetic screws were determined as CoCr < ZrO2 < Ti < PEEK. The highest Von Mises stress was 9584.4 Mpa in PEEK material on the prosthetic screw under 4 implant-oblique loading. The highest maximum principal stress value in bone was found to be 120.89 Mpa, for PEEK in 4 implant-oblique loading.
Conclusion: For four and six implant-supported structures, and depending on the loading condition, the system accumulated different stresses. The distribution of stress was reduced in materials with a high elastic modulus. When choosing materials for implant-supported fixed prostheses, it is essential to consider both the number of implants and the mechanical and physical attributes of the framework material.
Keywords: Biomechanics; Finite element analysis; Polyetheretherketone; Titanium; Zirconia.
© 2022 The Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Analysis of polyetheretherketone framework on the stress distribution of implant-supported fixed maxillary prosthesis: 3-D finite element analysis].Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2024 Aug;33(4):367-372. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39478392 Chinese.
-
Biomechanical behavior of titanium, cobalt-chromium, zirconia, and PEEK frameworks in implant-supported prostheses: a dynamic finite element analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Jan 18;25(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05486-5. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 39827102 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Using PEEK Copings and Different Restorative Materials on the Stress Distribution in Tooth-and-Implant-Supported Prostheses Under Static Loading: 3D FEA.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2025 May 29;40(3):371-381. doi: 10.11607/jomi.11005. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2025. PMID: 39093289
-
Investigation of Stress Distribution Between Two Different Implant Concepts in Implant- Supported Maxillary Prostheses with Different Framework Materials: A Finite Element Study.Int J Prosthodont. 2025 May 21;38(3):331-338. doi: 10.11607/ijp.9268. Int J Prosthodont. 2025. PMID: 39699968
-
Role of Polyetheretherketone in Prosthodontics: A Literature Review.Cureus. 2024 May 18;16(5):e60552. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60552. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38887343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Framework Material and Abutment Configuration on Fatigue Performance in Dental Implant Systems: A Finite Element Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Sep 6;60(9):1463. doi: 10.3390/medicina60091463. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39336504 Free PMC article.
-
The All-on-4 Concept Using Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)-Acrylic Resin Prostheses: Follow-Up Results of the Development Group at 5 Years and the Routine Group at One Year.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 9;11(11):3013. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11113013. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38002014 Free PMC article.
-
Finite element analysis of welded titanium bar and poly ether ether ketone bar in maxillary full arch splinted interim prosthesis.Sci Rep. 2025 May 9;15(1):16193. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99750-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40346189 Free PMC article.
-
Marginal gap of three-dimensional printed full-arch frameworks supported by all-on-four and all-on-six implant designs.J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2025 Jul 1;25(3):191-197. doi: 10.4103/jips.jips_40_25. Epub 2025 Jul 16. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2025. PMID: 40668990 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective study on the influence of inclination of cusp on implant marginal bone height in patients with periodontal disease.Acta Odontol Scand. 2024 Sep 12;83:493-499. doi: 10.2340/aos.v83.41226. Acta Odontol Scand. 2024. PMID: 39267359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Att W, Stappert C. Implant therapy to improve quality of life. Quintessence Int. 2003;34:573–581. - PubMed
-
- Heydecke G, Locker D, Awad MA, Lund JP, Feine JS. Oral and general health-related quality of life with conventional and implant dentures. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2003;31:161–168. - PubMed
-
- Resnik R, Misch CE. In: Misch’s contemporary implant dentistry. 4th ed. Resnik R, editor. Canada: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2020. Prosthetic options in implant dentistry; pp. 436–449.
-
- Maló P, Rangert B, Nobre M. All-on-4 immediate-function concept with Brånemark System implants for completely edentulous maxillae: a 1-year retrospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2005;7 Suppl 1:S88–S94. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

