High expression of KNL1 in prostate adenocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis and immune infiltration
- PMID: 36685823
- PMCID: PMC9853456
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1100787
High expression of KNL1 in prostate adenocarcinoma is associated with poor prognosis and immune infiltration
Abstract
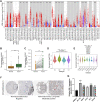
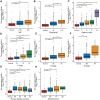
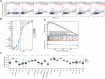
Prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) is a common malignancy with increasing morbidity and mortality. Kinetochore scaffold 1 (KNL1) has been reported to be involved in tumor progression and prognosis in other tumors, but its role in PRAD has not been reported in detail. KNL1 expression analysis, clinicopathological parameters analysis, prognostic correlation analysis, molecular interaction network and functional abdominal muscle analysis and immune infiltration analysis by using multiple online databases and downloaded expression profile. The results suggest that KNL1 is highly expressed in PRAD, which is associated with worse prognosis in PRAD patients. KnL1-related genes are highly enriched in mitotic function, which is considered to be highly related to the development of cancer. Finally, KNL1 expression is associated with a variety of tumor infiltrating immune cells, especially Treg and Th2 cells. In conclusion, our findings provide preliminary evidence that KNL1 may be an independent prognostic predictor of PRAD and is associated with immune infiltration.
Keywords: Knl1; bioinformatics analysis; immune infiltration; prognosis; prostate adenocarcinoma.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Ji, Wang, Dong, Pang, Fu, Wei and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

